Sooner or later, an information scientist informed that Ridge Regression was a sophisticated mannequin. As a result of he noticed that the coaching method is extra difficult.
Properly, that is precisely the target of my Machine Studying “Creation Calendar”, to make clear this type of complexity.
So, ile, we’ll discuss penalized variations of linear regression.
- First, we’ll see why the regularization or penalization is critical, and we’ll see how the mannequin is modified
- Then we’ll discover various kinds of regularization and their results.
- We will even practice the mannequin with regularization and take a look at completely different hyperparameters.
- We will even ask an extra query about the way to weight the weights within the penalization time period. (confused ? You will note)
Linear regression and its “circumstances”
After we discuss linear regression, folks usually point out that some circumstances must be happy.
You might have heard statements like:
- the residuals must be Gaussian (it’s generally confused with the goal being Gaussian, which is fake)
- the explanatory variables shouldn’t be collinear
In classical statistics, these circumstances are required for inference. In machine studying, the main focus is on prediction, so these assumptions are much less central, however the underlying points nonetheless exist.
Right here, we’ll see an instance of two options being collinear, and let’s make them fully equal.
And now we have the connection: y = x1 + x2, and x1 = x2
I do know that if they’re fully equal, we will simply do: y=2*x1. However the concept is to say they are often very related, and we will all the time construct a mannequin utilizing them, proper?
Then what’s the drawback?
When options are completely collinear, the answer just isn’t distinctive. Right here is an instance within the screenshot beneath.
y = 10000*x1 – 9998*x2

And we will discover that the norm of the coefficients is big.
So, the concept is to restrict the norm of the coefficients.
And after making use of the regularization, the conceptual mannequin is identical!
That’s proper. The parameters of the linear regression are modified. However the mannequin is identical.
Completely different Variations of Regularization
So the concept is to mix the MSE and the norm of the coefficients.
As a substitute of simply minimizing the MSE, we attempt to reduce the sum of the 2 phrases.
Which norm? We are able to do with norm L1, L2, and even mix them.
There are three classical methods to do that, and the corresponding mannequin names.
Ridge regression (L2 penalty)
Ridge regression provides a penalty on the squared values of the coefficients.
Intuitively:
- giant coefficients are closely penalized (due to the sq.)
- coefficients are pushed towards zero
- however they by no means turn into precisely zero
Impact:
- all options stay within the mannequin
- coefficients are smoother and extra steady
- very efficient towards collinearity
Ridge shrinks, however doesn’t choose.

Lasso regression (L1 penalty)
Lasso makes use of a unique penalty: the absolute worth of the coefficients.
This small change has a giant consequence.
With Lasso:
- some coefficients can turn into precisely zero
- the mannequin mechanically ignores some options
Because of this LASSO is named so, as a result of it stands for Least Absolute Shrinkage and Choice Operator.
- Operator: it refers back to the regularization operator added to the loss perform
- Least: it’s derived from a least-squares regression framework
- Absolute: it makes use of absolutely the worth of the coefficients (L1 norm)
- Shrinkage: it shrinks coefficients towards zero
- Choice: it might set some coefficients precisely to zero, performing function choice
Vital nuance:
- we will say that the mannequin nonetheless has the identical variety of coefficients
- however a few of them are compelled to zero throughout coaching
The mannequin kind is unchanged, however Lasso successfully removes options by driving coefficients to zero.

3. Elastic Web (L1 + L2)
Elastic Web is a mixture of Ridge and Lasso.
It makes use of:
- an L1 penalty (like Lasso)
- and an L2 penalty (like Ridge)
Why mix them?
As a result of:
- Lasso may be unstable when options are extremely correlated
- Ridge handles collinearity nicely however doesn’t choose options
Elastic Web offers a stability between:
- stability
- shrinkage
- sparsity
It’s usually essentially the most sensible selection in actual datasets.
What actually modifications: mannequin, coaching, tuning
Allow us to take a look at this from a Machine Studying perspective.
The mannequin does probably not change
For the mannequin, for all of the regularized variations, we nonetheless write:
y =a x + b.
- Identical variety of coefficients
- Identical prediction method
- However, the coefficients shall be completely different.
From a sure perspective, Ridge, Lasso, and Elastic Web are not completely different fashions.
The coaching precept can also be the identical
We nonetheless:
- outline a loss perform
- reduce it
- compute gradients
- replace coefficients
The one distinction is:
- the loss perform now features a penalty time period
That’s it.
The hyperparameters are added (that is the true distinction)
For Linear regression, we don’t have the management of the “complexity” of the mannequin.
- Customary linear regression: no hyperparameter
- Ridge: one hyperparameter (lambda)
- Lasso: one hyperparameter (lambda)
- Elastic Web: two hyperparameters
- one for general regularization energy
- one to stability L1 vs L2
So:
- commonplace linear regression doesn’t want tuning
- penalized regressions do
Because of this commonplace linear regression is commonly seen as “probably not Machine Studying”, whereas regularized variations clearly are.
Implementation of Regularized gradients
We preserve the gradient descent of OLS regression as reference, and for Ridge regression, we solely have so as to add the regularization time period for the coefficient.
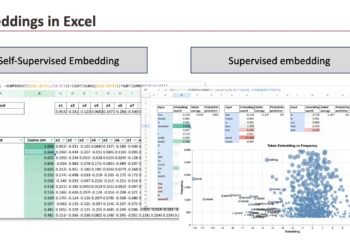
We’ll use a easy dataset that I generated (the identical one we already used for Linear Regression).
We are able to see the three “fashions” differ by way of coefficients. And the objective on this chapter is to implement the gradient for all of the fashions and evaluate them.

Ridge with penalized gradient
First, we will do for Ridge, and we solely have to alter the gradient of a.
Now, it doesn’t imply that the worth b just isn’t modified, because the gradient of b is every step relies upon additionally on a.

LASSO with penalized gradient
Then we will do the identical for LASSO.
And the one distinction can also be the gradient of a.
For every mannequin, we will additionally calculate the MSE and the regularized MSE. It’s fairly satisfying to see how they lower over the iterations.

Comparability of the coefficients
Now, we will visualize the coefficient a for all of the three fashions. With a view to see the variations, we enter very giant lambdas.

Affect of lambda
For giant worth of lambda, we’ll see that the coefficient a turns into small.
And if lambda LASSO turns into extraordinarily giant, then we theoretically get the worth of 0 for a. Numerically, now we have to enhance the gradient descent.

Regularized Logistic Regression?
We noticed Logistic Regression yesterday, and one query we will ask is that if it can be regularized. If sure, how are they referred to as?
The reply is after all sure, Logistic Regression may be regularized
Precisely the identical concept applies.
Logistic regression can be:
- L1 penalized
- L2 penalized
- Elastic Web penalized
There are no particular names like “Ridge Logistic Regression” in widespread utilization.
Why?
As a result of the idea is now not new.
In observe, libraries like scikit-learn merely allow you to specify:
- the loss perform
- the penalty sort
- the regularization energy
The naming mattered when the concept was new.
Now, regularization is simply a regular choice.
Different questions we will ask:
- Is regularization all the time helpful?
- How does the scaling of options affect the efficiency of regularized linear regression?
Conclusion
Ridge and Lasso don’t change the linear mannequin itself, they alter how the coefficients are realized. By including a penalty, regularization favors steady and significant options, particularly when options are correlated. Seeing this course of step-by-step in Excel makes it clear that these strategies usually are not extra advanced, simply extra managed.