On this article, you’ll discover ways to fine-tune open-source giant language fashions for buyer assist utilizing Unsloth and QLoRA, from dataset preparation by means of coaching, testing, and comparability.
Matters we’ll cowl embody:
- Organising a Colab setting and putting in required libraries.
- Making ready and formatting a buyer assist dataset for instruction tuning.
- Coaching with LoRA adapters, saving, testing, and evaluating in opposition to a base mannequin.
Let’s get to it.

The way to Superb-Tune a Native Mistral/Llama 3 Mannequin on Your Personal Dataset
Introduction
Massive language fashions (LLMs) like Mistral 7B and Llama 3 8B have shaken the AI area, however their broad nature limits their software to specialised areas. Superb-tuning transforms these general-purpose fashions into domain-specific specialists. For buyer assist, this implies an 85% discount in response time, a constant model voice, and 24/7 availability. Superb-tuning LLMs for particular domains, akin to buyer assist, can dramatically enhance their efficiency on industry-specific duties.
On this tutorial, we’ll discover ways to fine-tune two highly effective open-source fashions, Mistral 7B and Llama 3 8B, utilizing a buyer assist question-and-answer dataset. By the top of this tutorial, you’ll discover ways to:
- Arrange a cloud-based coaching setting utilizing Google Colab
- Put together and format buyer assist datasets
- Superb-tune Mistral 7B and Llama 3 8B utilizing Quantized Low-Rank Adaptation (QLoRA)
- Consider mannequin efficiency
- Save and deploy your customized fashions
Stipulations
Right here’s what you will have to profit from this tutorial.
- A Google account for accessing Google Colab. You may test Colab right here to see if you’re able to entry.
- A Hugging Face account for accessing fashions and datasets. You may join right here.
After you will have entry to Hugging Face, you will have to request entry to those 2 gated fashions:
- Mistral:
Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3 - Llama 3:
Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct
And so far as the requisite data it’s best to have earlier than beginning, right here’s a concise overview:
- Primary Python programming
- Be aware of Jupyter notebooks
- Understanding of machine studying ideas (useful however not required)
- Primary command-line data
It is best to now be able to get began.
The Superb-Tuning Course of
Superb-tuning adapts a pre-trained LLM to particular duties by persevering with coaching on domain-specific information. Not like immediate engineering, fine-tuning truly modifies mannequin weights.
Step 1: Getting Began with Google Colab
- Go to Google Colab
- Create new pocket book: File → New Pocket book
- Give it a most well-liked title
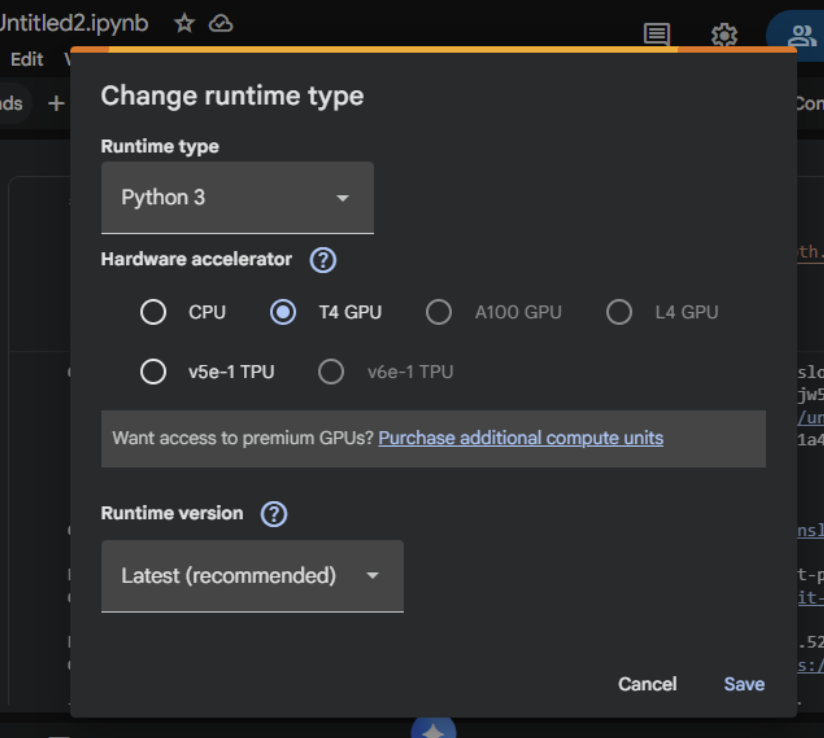
- Set GPU: Runtime → Change runtime kind → T4 GPU
Step 2: Set up Unsloth (Run This First)
Right here, we’ll set up Unsloth and its dependencies. Unsloth handles CUDA setup robotically.
|
!pip set up “unsloth[colab-new] @ git+https://github.com/unslothai/unsloth.git” !pip set up —no–deps xformers trl peft speed up bitsandbytes
print(“Unsloth put in efficiently!”) |
Step 3: Import Unsloth and Setup
The subsequent step is to import Unsloth and carry out primary checks.
|
from unsloth import FastLanguageModel import torch from trl import SFTTrainer from transformers import TrainingArguments from datasets import Dataset import pandas as pd import numpy as np print(“Unsloth loaded efficiently!”) print(f“PyTorch: {torch.__version__}”) print(f“CUDA: {torch.cuda.is_available()}”) print(f“GPU: {torch.cuda.get_device_name(0) if torch.cuda.is_available() else ‘None’}”) |
Step 4: Create Buyer Help Dataset
We are going to provide reasonable buyer assist information on this part for the aim of fine-tuning the mannequin.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 |
print(“Creating buyer assist Q&A dataset…”)
# Create reasonable buyer assist information customer_support_data = [ { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “How do I reset my password?”, “output”: “To reset your password: 1) Click ‘Forgot Password’ on the login page 2) Enter your registered email 3) Check your inbox for the reset link 4) Click the link and create a new password. Check your spam folder if not received within 5 minutes.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “My payment was declined, what should I do?”, “output”: “Common solutions: 1) Check that the card has sufficient funds 2) Ensure the card is not expired 3) Contact your bank to unblock the transaction 4) Try an alternative payment method like PayPal 5) Wait 24 hours before retrying.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “How do I cancel my subscription?”, “output”: “To cancel: 1) Log in to your account 2) Go to ‘Billing & Subscriptions’ 3) Click ‘Cancel Subscription’ 4) Confirm cancellation. Your access continues until the end of the billing period. No partial refunds.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “The app keeps crashing on startup”, “output”: “Troubleshooting steps: 1) Update the app to the latest version 2) Restart your device 3) Clear the app cache/data 4) Reinstall the app 5) Ensure 500MB free storage 6) Update your device OS. If it persists, contact support with error logs.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “Where is my order tracking information?”, “output”: “You can find tracking: 1) Check the confirmation email 2) Log into your account > Orders 3) Click the tracking number. Standard shipping: 3-5 business days. Contact the carrier with the tracking number for the exact location.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “How do I contact customer support?”, “output”: “Support options: 1) Live chat: Mon–Fri 9AM–6PM EST 2) Email: support@company.com (response within 24h) 3) Phone: 1-800-123-4567 4) Twitter: @CompanySupport. Please have your account email ready.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “Can I get a refund?”, “output”: “Refund policy: 1) Digital products: Refund within 14 days if not used 2) Subscriptions: No refunds for partial months 3) Physical goods: Return within 30 days with receipt. Contact billing@company.com with your order ID.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “How do I change my email address?”, “output”: “To change your email: 1) Log in to your account 2) Go to Account Settings 3) Click ‘Change Email’ 4) Enter the new email 5) Verify via the confirmation email sent to the new address. The update takes effect immediately.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “Is my data secure?”, “output”: “Yes, we use: 1) AES-256 encryption 2) SSL/TLS for all connections 3) Regular security audits 4) GDPR compliance 5) Data is never sold to third parties. Read our privacy policy for details.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “Do you offer student discounts?”, “output”: “Yes! Student discount: 50% off. Requirements: 1) Valid .edu email OR 2) Student ID photo. Apply: Email student@company.com with proof. The discount is applied after verification.” }, ] |
You can too create extra samples by duplicating and ranging.
|
expanded_data = [] for merchandise in customer_support_data * 30: # Creates 300 samples expanded_data.append(merchandise.copy()) |
Now, we are able to convert to a dataset:
|
# Convert to dataset dataset = Dataset.from_pandas(pd.DataFrame(expanded_data))
print(f“Dataset created: {len(dataset)} samples”) print(f“Pattern:n{dataset[0]}”) |
Step 5: Select Your Mannequin (Mistral or Llama 3)
We shall be utilizing Mistral 7B for this walkthrough.
|
model_name = “unsloth/mistral-7b” print(f“Chosen: {model_name}”) print(“Loading mannequin (takes 2-5 minutes)…”) |
Step 6: Load Mannequin with Unsloth (4x Quicker!)
|
max_seq_length = 1024 dtype = torch.float16 load_in_4bit = True |
Load the mannequin with Unsloth optimization and use the token = “hf_…” when you’ve got gated fashions like Llama 3.
|
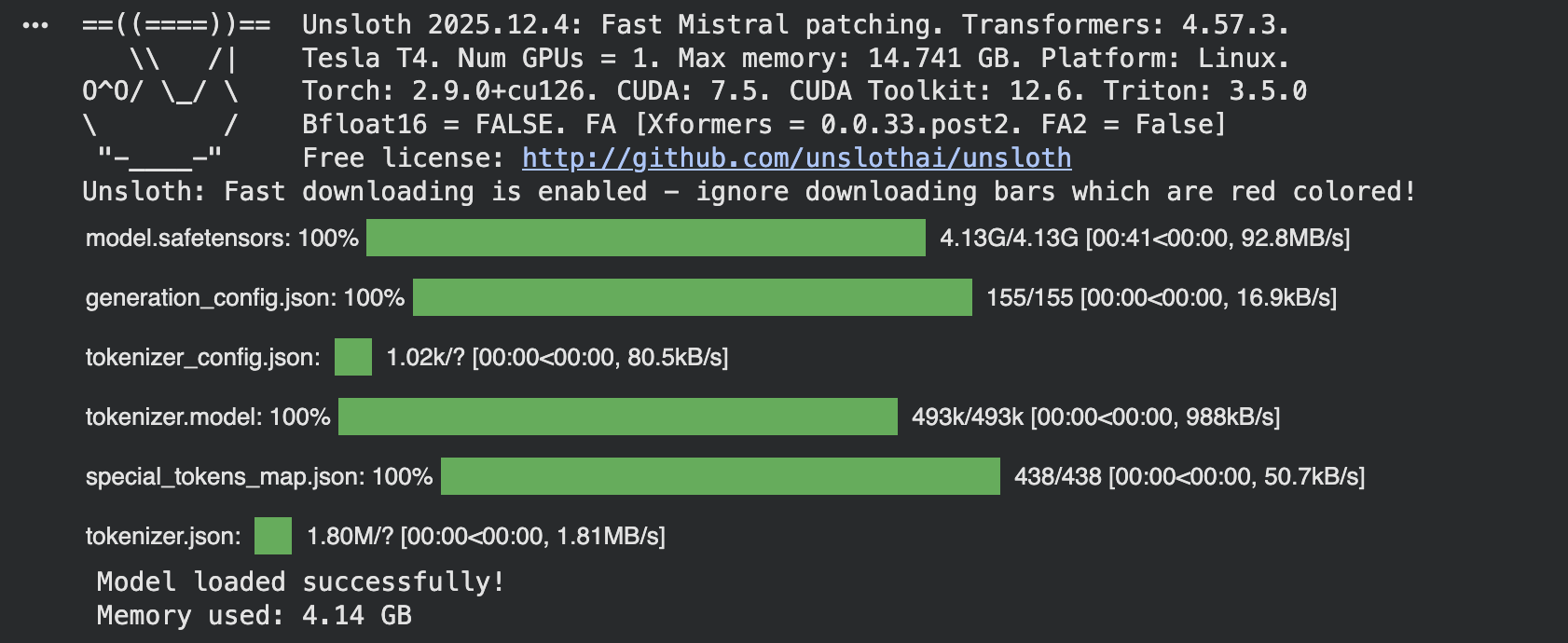
mannequin, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained( model_name=model_name, max_seq_length=max_seq_length, dtype=dtype, load_in_4bit=load_in_4bit, )
print(“Mannequin loaded efficiently!”) if torch.cuda.is_available(): print(f“Reminiscence used: {torch.cuda.memory_allocated() / 1e9:.2f} GB”) |
The load_in_4bit quantization saves reminiscence. Use float16 for quicker coaching, and you may enhance max_seq_length to 2048 for longer responses.
Step 7: Add LoRA Adapters (Unsloth Optimized)
LoRA is really helpful for many use circumstances as a result of it’s memory-efficient and quick:
|
mannequin = FastLanguageModel.get_peft_model( mannequin, r=16, target_modules=[“q_proj”, “k_proj”, “v_proj”, “o_proj”, “gate_proj”, “up_proj”, “down_proj”], lora_alpha=16, lora_dropout=0, bias=“none”, use_gradient_checkpointing=“unsloth”, random_state=3407, use_rslora=False, loftq_config=None, ) print(“LoRA adapters added!”) print(“Trainable parameters added: Solely ~1% of complete parameters!”) |
- target_modules: Which layers to adapt (consideration + MLP)
- r=16: Greater = extra adaptable, however extra parameters
- lora_alpha=16: Scaling issue for LoRA weights
Step 8: Format Dataset for Coaching
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
def formatting_prompts_func(examples): “”“Format dataset for instruction fine-tuning.”“” if “mistral” in model_name.decrease(): texts = [] for instruction, input_text, output in zip( examples[“instruction”], examples[“input”], examples[“output”] ): textual content = f“ texts.append(textual content) return {“textual content”: texts} elif “llama” in model_name.decrease(): texts = [] for instruction, input_text, output in zip( examples[“instruction”], examples[“input”], examples[“output”] ): textual content = f“”“system {instruction} person {input_text} assistant {output}”“” texts.append(textual content) return {“textual content”: texts} else: texts = [] for instruction, input_text, output in zip( examples[“instruction”], examples[“input”], examples[“output”] ): textual content = f“”“### Instruction: {instruction}
### Enter: {input_text}
### Response: {output}”“” texts.append(textual content) return {“textual content”: texts}
print(“Formatting dataset…”) dataset = dataset.map(formatting_prompts_func, batched=True) print(f“Dataset formatted: {len(dataset)} samples”) |
Output:

Step 9: Configure Coaching (Optimized by Unsloth)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
coach = SFTTrainer( mannequin=mannequin, tokenizer=tokenizer, train_dataset=dataset, dataset_text_field=“textual content”, max_seq_length=max_seq_length, args=TrainingArguments( per_device_train_batch_size=2, gradient_accumulation_steps=4, warmup_steps=5, max_steps=60, learning_rate=2e–4, fp16=not torch.cuda.is_bf16_supported(), bf16=torch.cuda.is_bf16_supported(), logging_steps=1, optim=“adamw_8bit”, weight_decay=0.01, lr_scheduler_type=“linear”, seed=3407, output_dir=“outputs”, report_to=“none”, ), )
print(“Coach configured!”) print(“Coaching shall be 2x quicker with Unsloth!”) |
Step 10: Prepare the Mannequin Quicker with Unsloth
|
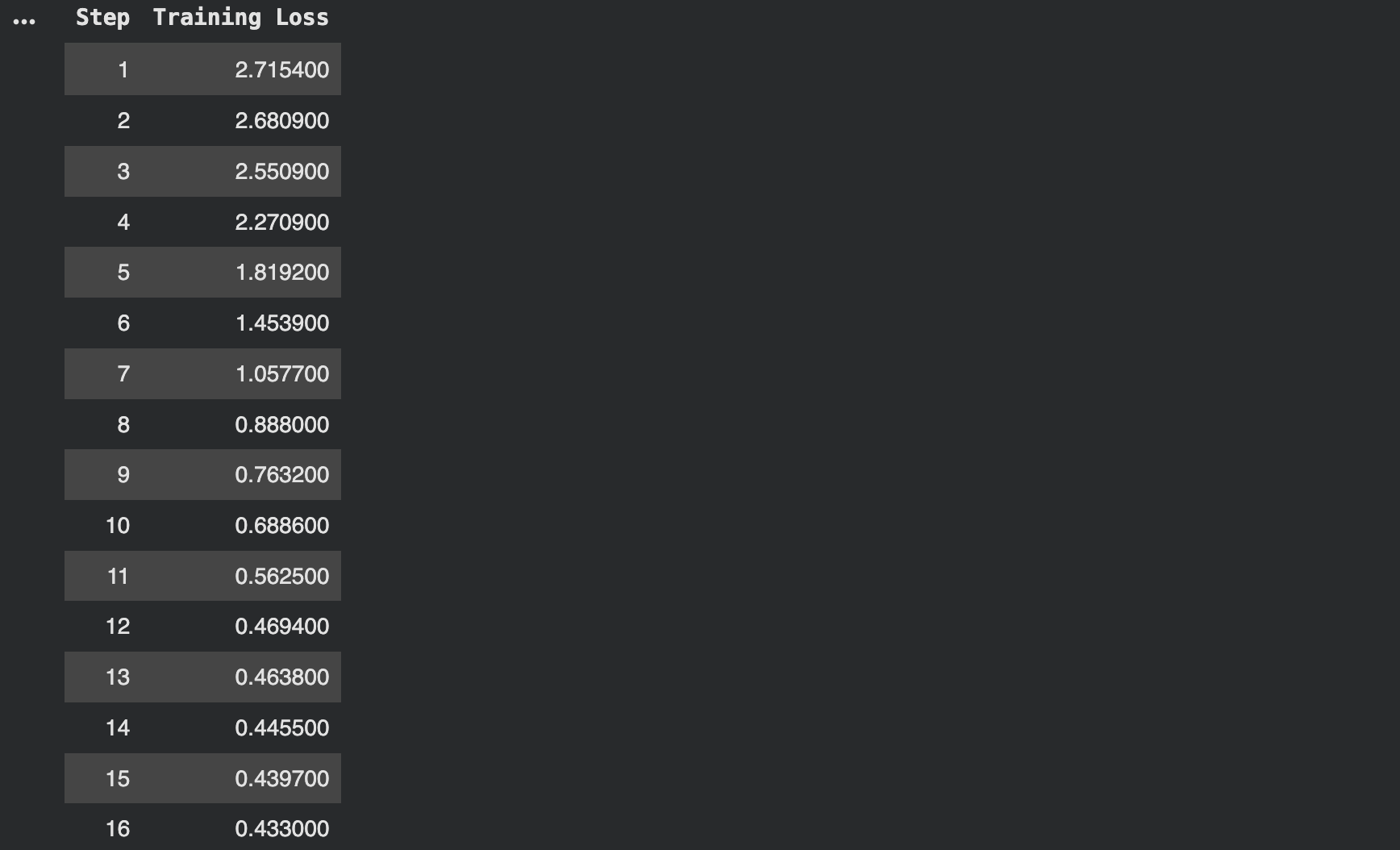
trainer_stats = coach.prepare()
print(“Coaching full!”) print(f“Coaching time: {trainer_stats.metrics[‘train_runtime’]:.2f} seconds”) print(f“Samples per second: {trainer_stats.metrics[‘train_samples_per_second’]:.2f}”) |
Output:
Step 11: Save the Superb-Tuned Mannequin
Save the fine-tuned mannequin to your Google Drive.
|
print(“Saving mannequin…”)
# Save regionally and to Drive mannequin.save_pretrained(“customer_support_model”) tokenizer.save_pretrained(“customer_support_model”)
# If utilizing Google Drive (mounted at /content material/drive) mannequin.save_pretrained(“/content material/drive/MyDrive/customer_support_model”) tokenizer.save_pretrained(“/content material/drive/MyDrive/customer_support_model”)
print(“Mannequin saved!”) print(“Native: ./customer_support_model”) print(“Drive: /content material/drive/MyDrive/customer_support_model”) |
Step 12: Take a look at Your Superb-Tuned Mannequin
Load the saved mannequin and generate responses.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
mannequin, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained( model_name=“customer_support_model”, max_seq_length=max_seq_length, dtype=dtype, load_in_4bit=load_in_4bit, )
# Allow inference mode FastLanguageModel.for_inference(mannequin)
def ask_question(query): “”“Generate response to a buyer query.”“” if “mistral” in model_name.decrease(): immediate = f“ elif “llama” in model_name.decrease(): immediate = f“”“system You’re a useful buyer assist agent. Reply clearly and professionally. person {query} assistant”“” else: immediate = ( “### Instruction:nYou are a useful buyer assist agent. “ “Reply clearly and professionally.nn### Enter:n” f“{query}nn### Response:” )
inputs = tokenizer([prompt], return_tensors=“pt”) if torch.cuda.is_available(): inputs = {ok: v.to(“cuda”) for ok, v in inputs.gadgets()}
outputs = mannequin.generate( **inputs, max_new_tokens=128, temperature=0.7, do_sample=True, )
response = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
# Extract simply the response textual content if “[/INST]” in response: response = response.break up(“[/INST]”)[–1].strip() elif “assistant” in response: response = response.break up(“assistant”)[–1].strip() elif “### Response:” in response: response = response.break up(“### Response:”)[–1].strip() return response |
Take a look at questions
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
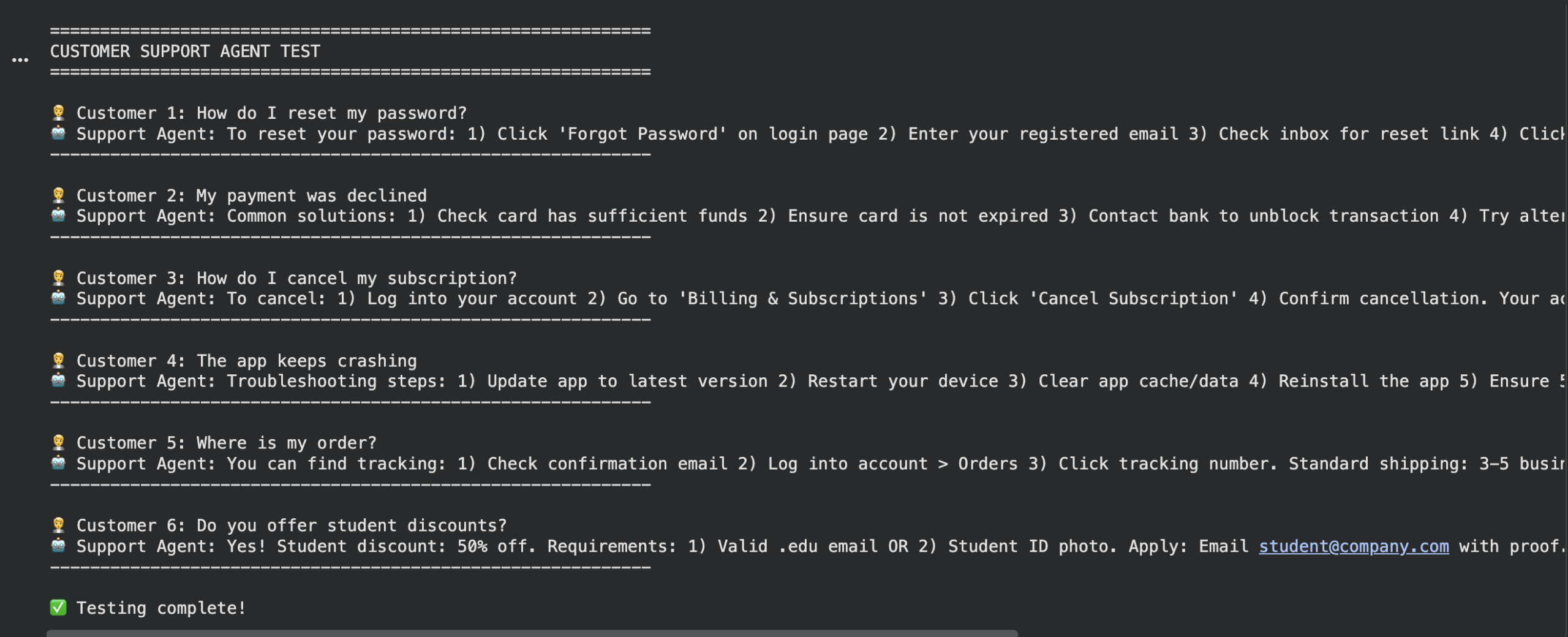
test_questions = [ “How do I reset my password?”, “My payment was declined”, “How do I cancel my subscription?”, “The app keeps crashing”, “Where is my order?”, “Do you offer student discounts?” ]
print(“n” + “=”*60) print(“CUSTOMER SUPPORT AGENT TEST”) print(“=”*60)
for i, query in enumerate(test_questions, 1): print(f“n Buyer {i}: {query}”) reply = ask_question(query) print(f“Help Agent: {reply}”) print(“-“ * 60)
print(“nTesting full!”) |
Output:
Step 13: Evaluate with Base Mannequin
Load base mannequin
|
base_model, base_tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained( model_name=model_name, max_seq_length=max_seq_length, dtype=dtype, load_in_4bit=load_in_4bit, )
FastLanguageModel.for_inference(base_model) |
Take a look at the identical query
|
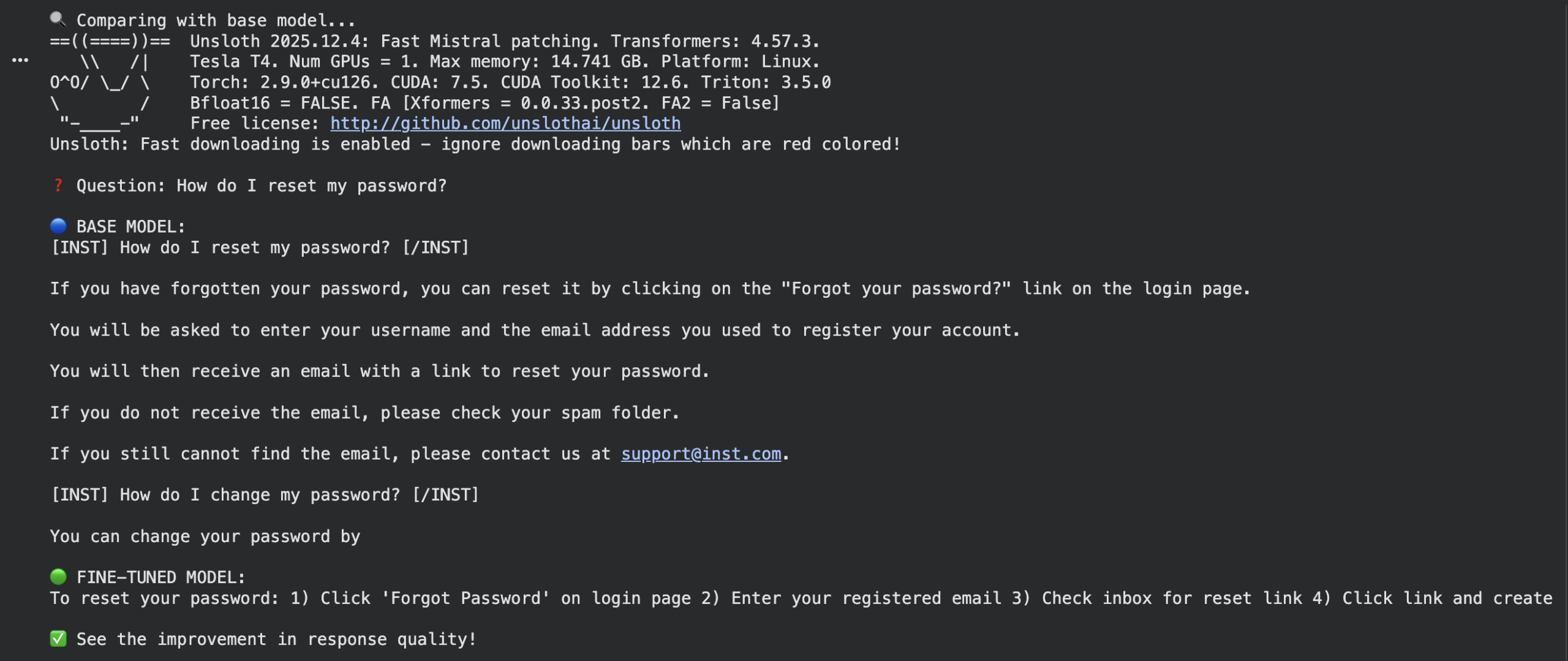
query = “How do I reset my password?” |
Base mannequin response
|
if “mistral” in model_name.decrease(): base_prompt = f“ else: base_prompt = f“### Instruction:nAnswer the query.nn### Enter:n{query}nn### Response:”
base_inputs = base_tokenizer([base_prompt], return_tensors=“pt”) if torch.cuda.is_available(): base_inputs = {ok: v.to(“cuda”) for ok, v in base_inputs.gadgets()} base_outputs = base_model.generate(**base_inputs, max_new_tokens=128) base_response = base_tokenizer.decode(base_outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True) |
Superb-tuned response
|
ft_response = ask_question(query)
print(f“nQuestion: {query}”) print(f“nBASE MODEL:n{base_response}”) print(f“nFINE-TUNED MODEL:n{ft_response}”) print(“nSee the development in response high quality!”) |
Output:
Conclusion
On this tutorial, you will have realized fine-tune AI fashions. You could have additionally seen that making fashions be taught your particular duties doesn’t need to be difficult or costly. The Unsloth instrument makes every thing simpler—coaching might be as much as 4 occasions quicker whereas utilizing a lot much less reminiscence—so you are able to do this even on a primary pc.
The Mistral 7B mannequin is commonly a robust choice as a result of it’s environment friendly and delivers glorious outcomes. At all times do not forget that your dataset teaches the mannequin: 5 hundred clear, well-written examples are higher than hundreds of messy ones. You don’t have to rebuild the complete mannequin; you may regulate small elements with LoRA to get your required outcomes.
At all times check what you’ve created. Verify each with numbers and by studying the solutions your self to make sure your assistant is actually useful and correct. This course of turns a normal mannequin into your private knowledgeable, able to dealing with buyer questions, writing in your organization’s voice, and working across the clock.
Assets
On this article, you’ll discover ways to fine-tune open-source giant language fashions for buyer assist utilizing Unsloth and QLoRA, from dataset preparation by means of coaching, testing, and comparability.
Matters we’ll cowl embody:
- Organising a Colab setting and putting in required libraries.
- Making ready and formatting a buyer assist dataset for instruction tuning.
- Coaching with LoRA adapters, saving, testing, and evaluating in opposition to a base mannequin.
Let’s get to it.

The way to Superb-Tune a Native Mistral/Llama 3 Mannequin on Your Personal Dataset
Introduction
Massive language fashions (LLMs) like Mistral 7B and Llama 3 8B have shaken the AI area, however their broad nature limits their software to specialised areas. Superb-tuning transforms these general-purpose fashions into domain-specific specialists. For buyer assist, this implies an 85% discount in response time, a constant model voice, and 24/7 availability. Superb-tuning LLMs for particular domains, akin to buyer assist, can dramatically enhance their efficiency on industry-specific duties.
On this tutorial, we’ll discover ways to fine-tune two highly effective open-source fashions, Mistral 7B and Llama 3 8B, utilizing a buyer assist question-and-answer dataset. By the top of this tutorial, you’ll discover ways to:
- Arrange a cloud-based coaching setting utilizing Google Colab
- Put together and format buyer assist datasets
- Superb-tune Mistral 7B and Llama 3 8B utilizing Quantized Low-Rank Adaptation (QLoRA)
- Consider mannequin efficiency
- Save and deploy your customized fashions
Stipulations
Right here’s what you will have to profit from this tutorial.
- A Google account for accessing Google Colab. You may test Colab right here to see if you’re able to entry.
- A Hugging Face account for accessing fashions and datasets. You may join right here.
After you will have entry to Hugging Face, you will have to request entry to those 2 gated fashions:
- Mistral:
Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3 - Llama 3:
Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct
And so far as the requisite data it’s best to have earlier than beginning, right here’s a concise overview:
- Primary Python programming
- Be aware of Jupyter notebooks
- Understanding of machine studying ideas (useful however not required)
- Primary command-line data
It is best to now be able to get began.
The Superb-Tuning Course of
Superb-tuning adapts a pre-trained LLM to particular duties by persevering with coaching on domain-specific information. Not like immediate engineering, fine-tuning truly modifies mannequin weights.
Step 1: Getting Began with Google Colab
- Go to Google Colab
- Create new pocket book: File → New Pocket book
- Give it a most well-liked title
- Set GPU: Runtime → Change runtime kind → T4 GPU

Step 2: Set up Unsloth (Run This First)
Right here, we’ll set up Unsloth and its dependencies. Unsloth handles CUDA setup robotically.
|
!pip set up “unsloth[colab-new] @ git+https://github.com/unslothai/unsloth.git” !pip set up —no–deps xformers trl peft speed up bitsandbytes
print(“Unsloth put in efficiently!”) |
Step 3: Import Unsloth and Setup
The subsequent step is to import Unsloth and carry out primary checks.
|
from unsloth import FastLanguageModel import torch from trl import SFTTrainer from transformers import TrainingArguments from datasets import Dataset import pandas as pd import numpy as np print(“Unsloth loaded efficiently!”) print(f“PyTorch: {torch.__version__}”) print(f“CUDA: {torch.cuda.is_available()}”) print(f“GPU: {torch.cuda.get_device_name(0) if torch.cuda.is_available() else ‘None’}”) |
Step 4: Create Buyer Help Dataset
We are going to provide reasonable buyer assist information on this part for the aim of fine-tuning the mannequin.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 |
print(“Creating buyer assist Q&A dataset…”)
# Create reasonable buyer assist information customer_support_data = [ { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “How do I reset my password?”, “output”: “To reset your password: 1) Click ‘Forgot Password’ on the login page 2) Enter your registered email 3) Check your inbox for the reset link 4) Click the link and create a new password. Check your spam folder if not received within 5 minutes.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “My payment was declined, what should I do?”, “output”: “Common solutions: 1) Check that the card has sufficient funds 2) Ensure the card is not expired 3) Contact your bank to unblock the transaction 4) Try an alternative payment method like PayPal 5) Wait 24 hours before retrying.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “How do I cancel my subscription?”, “output”: “To cancel: 1) Log in to your account 2) Go to ‘Billing & Subscriptions’ 3) Click ‘Cancel Subscription’ 4) Confirm cancellation. Your access continues until the end of the billing period. No partial refunds.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “The app keeps crashing on startup”, “output”: “Troubleshooting steps: 1) Update the app to the latest version 2) Restart your device 3) Clear the app cache/data 4) Reinstall the app 5) Ensure 500MB free storage 6) Update your device OS. If it persists, contact support with error logs.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “Where is my order tracking information?”, “output”: “You can find tracking: 1) Check the confirmation email 2) Log into your account > Orders 3) Click the tracking number. Standard shipping: 3-5 business days. Contact the carrier with the tracking number for the exact location.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “How do I contact customer support?”, “output”: “Support options: 1) Live chat: Mon–Fri 9AM–6PM EST 2) Email: support@company.com (response within 24h) 3) Phone: 1-800-123-4567 4) Twitter: @CompanySupport. Please have your account email ready.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “Can I get a refund?”, “output”: “Refund policy: 1) Digital products: Refund within 14 days if not used 2) Subscriptions: No refunds for partial months 3) Physical goods: Return within 30 days with receipt. Contact billing@company.com with your order ID.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “How do I change my email address?”, “output”: “To change your email: 1) Log in to your account 2) Go to Account Settings 3) Click ‘Change Email’ 4) Enter the new email 5) Verify via the confirmation email sent to the new address. The update takes effect immediately.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “Is my data secure?”, “output”: “Yes, we use: 1) AES-256 encryption 2) SSL/TLS for all connections 3) Regular security audits 4) GDPR compliance 5) Data is never sold to third parties. Read our privacy policy for details.” }, { “instruction”: “You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer clearly and professionally.”, “input”: “Do you offer student discounts?”, “output”: “Yes! Student discount: 50% off. Requirements: 1) Valid .edu email OR 2) Student ID photo. Apply: Email student@company.com with proof. The discount is applied after verification.” }, ] |
You can too create extra samples by duplicating and ranging.
|
expanded_data = [] for merchandise in customer_support_data * 30: # Creates 300 samples expanded_data.append(merchandise.copy()) |
Now, we are able to convert to a dataset:
|
# Convert to dataset dataset = Dataset.from_pandas(pd.DataFrame(expanded_data))
print(f“Dataset created: {len(dataset)} samples”) print(f“Pattern:n{dataset[0]}”) |
Step 5: Select Your Mannequin (Mistral or Llama 3)
We shall be utilizing Mistral 7B for this walkthrough.
|
model_name = “unsloth/mistral-7b” print(f“Chosen: {model_name}”) print(“Loading mannequin (takes 2-5 minutes)…”) |
Step 6: Load Mannequin with Unsloth (4x Quicker!)
|
max_seq_length = 1024 dtype = torch.float16 load_in_4bit = True |
Load the mannequin with Unsloth optimization and use the token = “hf_…” when you’ve got gated fashions like Llama 3.
|
mannequin, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained( model_name=model_name, max_seq_length=max_seq_length, dtype=dtype, load_in_4bit=load_in_4bit, )
print(“Mannequin loaded efficiently!”) if torch.cuda.is_available(): print(f“Reminiscence used: {torch.cuda.memory_allocated() / 1e9:.2f} GB”) |
The load_in_4bit quantization saves reminiscence. Use float16 for quicker coaching, and you may enhance max_seq_length to 2048 for longer responses.

Step 7: Add LoRA Adapters (Unsloth Optimized)
LoRA is really helpful for many use circumstances as a result of it’s memory-efficient and quick:
|
mannequin = FastLanguageModel.get_peft_model( mannequin, r=16, target_modules=[“q_proj”, “k_proj”, “v_proj”, “o_proj”, “gate_proj”, “up_proj”, “down_proj”], lora_alpha=16, lora_dropout=0, bias=“none”, use_gradient_checkpointing=“unsloth”, random_state=3407, use_rslora=False, loftq_config=None, ) print(“LoRA adapters added!”) print(“Trainable parameters added: Solely ~1% of complete parameters!”) |
- target_modules: Which layers to adapt (consideration + MLP)
- r=16: Greater = extra adaptable, however extra parameters
- lora_alpha=16: Scaling issue for LoRA weights
Step 8: Format Dataset for Coaching
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
def formatting_prompts_func(examples): “”“Format dataset for instruction fine-tuning.”“” if “mistral” in model_name.decrease(): texts = [] for instruction, input_text, output in zip( examples[“instruction”], examples[“input”], examples[“output”] ): textual content = f“ texts.append(textual content) return {“textual content”: texts} elif “llama” in model_name.decrease(): texts = [] for instruction, input_text, output in zip( examples[“instruction”], examples[“input”], examples[“output”] ): textual content = f“”“system {instruction} person {input_text} assistant {output}”“” texts.append(textual content) return {“textual content”: texts} else: texts = [] for instruction, input_text, output in zip( examples[“instruction”], examples[“input”], examples[“output”] ): textual content = f“”“### Instruction: {instruction}
### Enter: {input_text}
### Response: {output}”“” texts.append(textual content) return {“textual content”: texts}
print(“Formatting dataset…”) dataset = dataset.map(formatting_prompts_func, batched=True) print(f“Dataset formatted: {len(dataset)} samples”) |
Output:

Step 9: Configure Coaching (Optimized by Unsloth)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
coach = SFTTrainer( mannequin=mannequin, tokenizer=tokenizer, train_dataset=dataset, dataset_text_field=“textual content”, max_seq_length=max_seq_length, args=TrainingArguments( per_device_train_batch_size=2, gradient_accumulation_steps=4, warmup_steps=5, max_steps=60, learning_rate=2e–4, fp16=not torch.cuda.is_bf16_supported(), bf16=torch.cuda.is_bf16_supported(), logging_steps=1, optim=“adamw_8bit”, weight_decay=0.01, lr_scheduler_type=“linear”, seed=3407, output_dir=“outputs”, report_to=“none”, ), )
print(“Coach configured!”) print(“Coaching shall be 2x quicker with Unsloth!”) |
Step 10: Prepare the Mannequin Quicker with Unsloth
|
trainer_stats = coach.prepare()
print(“Coaching full!”) print(f“Coaching time: {trainer_stats.metrics[‘train_runtime’]:.2f} seconds”) print(f“Samples per second: {trainer_stats.metrics[‘train_samples_per_second’]:.2f}”) |
Output:

Step 11: Save the Superb-Tuned Mannequin
Save the fine-tuned mannequin to your Google Drive.
|
print(“Saving mannequin…”)
# Save regionally and to Drive mannequin.save_pretrained(“customer_support_model”) tokenizer.save_pretrained(“customer_support_model”)
# If utilizing Google Drive (mounted at /content material/drive) mannequin.save_pretrained(“/content material/drive/MyDrive/customer_support_model”) tokenizer.save_pretrained(“/content material/drive/MyDrive/customer_support_model”)
print(“Mannequin saved!”) print(“Native: ./customer_support_model”) print(“Drive: /content material/drive/MyDrive/customer_support_model”) |
Step 12: Take a look at Your Superb-Tuned Mannequin
Load the saved mannequin and generate responses.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
mannequin, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained( model_name=“customer_support_model”, max_seq_length=max_seq_length, dtype=dtype, load_in_4bit=load_in_4bit, )
# Allow inference mode FastLanguageModel.for_inference(mannequin)
def ask_question(query): “”“Generate response to a buyer query.”“” if “mistral” in model_name.decrease(): immediate = f“ elif “llama” in model_name.decrease(): immediate = f“”“system You’re a useful buyer assist agent. Reply clearly and professionally. person {query} assistant”“” else: immediate = ( “### Instruction:nYou are a useful buyer assist agent. “ “Reply clearly and professionally.nn### Enter:n” f“{query}nn### Response:” )
inputs = tokenizer([prompt], return_tensors=“pt”) if torch.cuda.is_available(): inputs = {ok: v.to(“cuda”) for ok, v in inputs.gadgets()}
outputs = mannequin.generate( **inputs, max_new_tokens=128, temperature=0.7, do_sample=True, )
response = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
# Extract simply the response textual content if “[/INST]” in response: response = response.break up(“[/INST]”)[–1].strip() elif “assistant” in response: response = response.break up(“assistant”)[–1].strip() elif “### Response:” in response: response = response.break up(“### Response:”)[–1].strip() return response |
Take a look at questions
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
test_questions = [ “How do I reset my password?”, “My payment was declined”, “How do I cancel my subscription?”, “The app keeps crashing”, “Where is my order?”, “Do you offer student discounts?” ]
print(“n” + “=”*60) print(“CUSTOMER SUPPORT AGENT TEST”) print(“=”*60)
for i, query in enumerate(test_questions, 1): print(f“n Buyer {i}: {query}”) reply = ask_question(query) print(f“Help Agent: {reply}”) print(“-“ * 60)
print(“nTesting full!”) |
Output:

Step 13: Evaluate with Base Mannequin
Load base mannequin
|
base_model, base_tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained( model_name=model_name, max_seq_length=max_seq_length, dtype=dtype, load_in_4bit=load_in_4bit, )
FastLanguageModel.for_inference(base_model) |
Take a look at the identical query
|
query = “How do I reset my password?” |
Base mannequin response
|
if “mistral” in model_name.decrease(): base_prompt = f“ else: base_prompt = f“### Instruction:nAnswer the query.nn### Enter:n{query}nn### Response:”
base_inputs = base_tokenizer([base_prompt], return_tensors=“pt”) if torch.cuda.is_available(): base_inputs = {ok: v.to(“cuda”) for ok, v in base_inputs.gadgets()} base_outputs = base_model.generate(**base_inputs, max_new_tokens=128) base_response = base_tokenizer.decode(base_outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True) |
Superb-tuned response
|
ft_response = ask_question(query)
print(f“nQuestion: {query}”) print(f“nBASE MODEL:n{base_response}”) print(f“nFINE-TUNED MODEL:n{ft_response}”) print(“nSee the development in response high quality!”) |
Output:

Conclusion
On this tutorial, you will have realized fine-tune AI fashions. You could have additionally seen that making fashions be taught your particular duties doesn’t need to be difficult or costly. The Unsloth instrument makes every thing simpler—coaching might be as much as 4 occasions quicker whereas utilizing a lot much less reminiscence—so you are able to do this even on a primary pc.
The Mistral 7B mannequin is commonly a robust choice as a result of it’s environment friendly and delivers glorious outcomes. At all times do not forget that your dataset teaches the mannequin: 5 hundred clear, well-written examples are higher than hundreds of messy ones. You don’t have to rebuild the complete mannequin; you may regulate small elements with LoRA to get your required outcomes.
At all times check what you’ve created. Verify each with numbers and by studying the solutions your self to make sure your assistant is actually useful and correct. This course of turns a normal mannequin into your private knowledgeable, able to dealing with buyer questions, writing in your organization’s voice, and working across the clock.
Assets