Intro
how you can study and manipulate an LLM’s neural community. That is the subject of mechanistic interpretability analysis, and it will possibly reply many thrilling questions.
Bear in mind: An LLM is a deep synthetic neural community, made up of neurons and weights that decide how strongly these neurons are related. What makes a neural community arrive at its conclusion? How a lot of the data it processes does it contemplate and analyze adequately?
These types of questions have been investigated in an unlimited variety of publications at the very least since deep neural networks began displaying promise. To be clear, mechanistic interpretability existed earlier than LLMs did, and was already an thrilling facet of Explainable AI analysis with earlier deep neural networks. As an example, figuring out the salient options that set off a CNN to reach at a given object classification or automobile steering route may also help us perceive how reliable and dependable the community is in safety-critical conditions.
However with LLMs, the subject actually took off, and have become rather more fascinating. Are the human-like cognitive skills of LLMs actual or pretend? How does data journey via the neural community? Is there hidden data inside an LLM?
On this put up, you will discover:
- A refresher on LLM structure
- An introduction to interpretability strategies
- Use instances
- A dialogue of previous analysis
In a follow-up article, we are going to have a look at Python code to use a few of these expertise, visualize the activations of the neural community and extra.
Refresher: The design of an LLM
For the aim of this text, we’d like a fundamental understanding of the spots within the neural community the place it’s price hooking into, to derive presumably helpful data within the course of. Subsequently, this part is a fast reminder of the parts of an LLM.
LLMs use a sequence of enter tokens to foretell the subsequent token.

Tokenizer: Initially, sentences are segmented into tokens. The aim of the token vocabulary is to show continuously used sub-words into single tokens. Every token has a singular ID.
Nevertheless, tokens might be complicated and messy since they supply an inaccurate illustration of many issues, together with numbers and particular person characters. Asking an LLM to calculate or to rely letters is a fairly unfair factor to do. (With specialised embedding schemes, their efficiency can enhance [1].)
Embedding: A glance-up desk is used to assign every token ID to an embedding vector of a given dimensionality. The look-up desk is discovered (i.e., derived through the neural community coaching), and tends to put co-occurring tokens nearer collectively within the embedding house. The dimensionality of the embedding vectors is a crucial trade-off between the capabilities of LLMs and computing effort. Because the order of the tokens would in any other case not be obvious in subsequent steps, positional encoding is added to those embeddings. In rotary positional encoding, the cosine of the token place can be utilized. The embedding vectors of all enter tokens present the matrix that the LLM processes, the preliminary hidden states. Because the LLM operates with this matrix, which strikes via layers because the residual stream (additionally known as the hidden state or illustration house), it really works in latent house.
Modalities apart from textual content: LLMs can work with modalities apart from textual content. In these instances, the tokenizer and embedding are modified to accommodate completely different modalities, similar to sound or photographs.
Transformer blocks: A lot of transformer blocks (dozens) refine the residual stream, including context and extra that means. Every transformer layer consists of an consideration part [2] and an MLP part. These parts are fed the normalized hidden state. The output is then added to the residual stream.
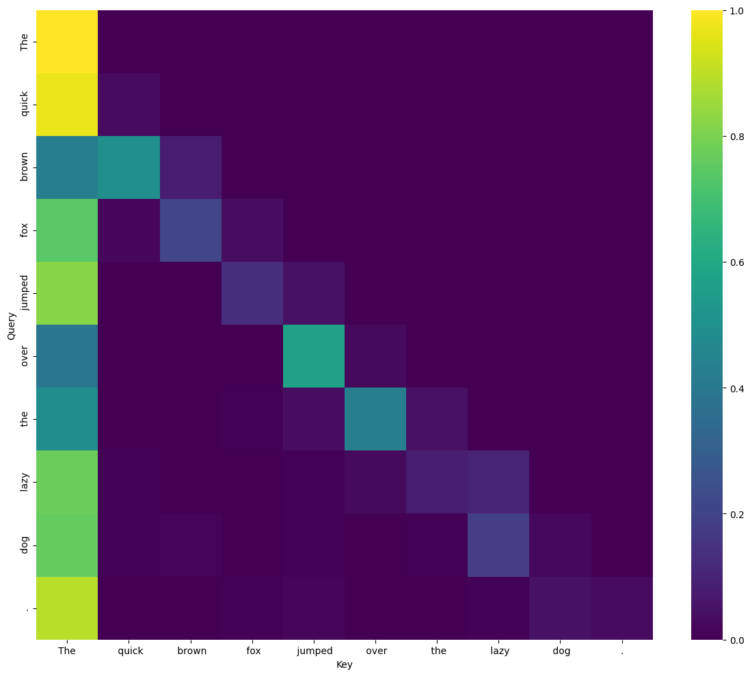
- Consideration: A number of consideration heads (additionally dozens) add weighted data from supply tokens to vacation spot tokens (within the residual stream). Every consideration head’s “nature” is parametrized via three discovered matrices WQ, WOkay, WV, which basically determine what the eye head is specialised on. Queries, keys and values are calculated by multiplying these matrices with the hidden states for all tokens. The eye weight are then computed for every vacation spot token from the softmax of the scaled dot merchandise of the question and the important thing vectors of the supply tokens. This consideration weight describes the power of the connection between the supply and the vacation spot for a given specialization of the eye head. Lastly, the pinnacle outputs a weighted sum of the supply token’s worth vectors, and all the pinnacle’s outputs are concatenated and handed via a discovered output projection WO.
- MLP: A totally related feedforward community. This linear-nonlinear-linear operation is utilized independently at every place. MLP networks usually include a big share of the parameters in an LLM.
MLP networks retailer a lot of the data. Later layers are likely to include extra semantic and fewer shallow data [3]. That is related when deciding the place to probe or intervene. (With some effort, these data representations might be modified in a educated LLM via weight modification [4] or residual stream intervention [5].)
Unembedding: The ultimate residual stream values are normalized and linearly mapped again to the vocabulary dimension to supply the logits for every enter token place. Usually, we solely want the prediction for the token following the final enter token, so we use that one. The softmax perform converts the logits for the ultimate place right into a likelihood distribution. One possibility is then chosen from this distribution (e.g., the most certainly or a sampling-based possibility) as the subsequent predicted token.
In case you want to study extra about how LLMs work and achieve extra instinct, Stephen McAleese’s [6] clarification is superb.
Now that we seemed on the structure, the query to ask is: What do the intermittent states of the residual stream imply? How do they relate to the LLM’s output? Why does this work?
Introduction to interpretability strategies
Let’s check out our toolbox. Which parts will assist us reply our questions, and which strategies can we apply to investigate them? Our choices embody:
- Neurons:
We might observe the activation of particular person neurons. - Consideration:
We might observe the output of particular person consideration heads in every layer.
We might observe the queries, keys, values and a focus weights of every consideration head for every place and layer.
We might observe the concatenated outputs of all consideration heads in every layer. - MLP:
We might observe the MLP output in every layer.
We might observe the neural activations inside the MLP networks.
We might observe the LayerNorm imply/variance to trace scale, saturation and outliers. - Residual stream:
We might observe the residual stream at every place, in every layer.
We might unembed the residual stream in intermediate layers, to look at what would occur if we stopped there — earlier layers usually yield extra shallow predictions. (It is a helpful diagnostic, however not absolutely dependable — the unembedding mapping was educated for the ultimate layer.)
We will additionally derive extra data:
- Linear probes and classifiers: We will construct a system that classifies the recorded residual stream into one group or one other, or measures some function inside it.
- Gradient-based attributions: We will compute the gradient of a selected output with respect to some or the entire neural values. The gradient magnitude signifies how delicate the prediction is to modifications in these values.
All of this may be accomplished whereas a given, static LLM runs an inference on a given immediate or whereas we actively intervene:
- Comparability of a number of inferences: We will change, practice, modify or change the LLM or have it course of completely different prompts, and document the aforementioned data.
- Ablation: We will zero out neurons, heads, MLP blocks or vectors within the residual stream and watch the way it impacts conduct. For instance, this enables us to measure the contribution of a head, neuron or pathway to token prediction.
- Steering: We will actively steer the LLM by changing or in any other case modifying activations within the residual stream.
Use instances
The interpretability strategies mentioned signify an unlimited arsenal that may be utilized to many alternative use instances.
- Mannequin efficiency enchancment or conduct steering via activation steering: As an example, along with a system immediate, a mannequin’s conduct might be steered in direction of a sure trait or focus dynamically, with out altering the mannequin.
- Explainability: Strategies similar to steering vectors, sparse autoencoders, and circuit tracing can be utilized to grasp what the mannequin does and why based mostly on its activations.
- Security: Detecting and discouraging undesirable options throughout coaching or implementing run-time supervision to interrupt a mannequin that’s deviating. Detect new or dangerous capabilities.
- Drift detection: Throughout mannequin growth, you will need to perceive when a newly educated mannequin is behaving in another way and to what extent.
- Coaching enchancment: Understanding the contribution of elements of the mannequin’s conduct to its total efficiency optimizes mannequin growth. For instance, pointless Chain-of-Thought steps might be discouraged throughout coaching, which results in smaller, quicker, or probably extra highly effective fashions.
- Scientific and linguistic learnings: Use the fashions as an object to review to raised perceive AI, language acquisition and cognition.
LLM interpretability analysis
The sphere of interpretability has steadily developed over the previous few years, answering thrilling questions alongside the way in which. Simply three years in the past, it was unclear whether or not or not the learnings outlined under would manifest. It is a transient historical past of key insights:
- In-context studying and sample understanding: Throughout LLM coaching, some consideration heads achieve the potential to collaborate as sample identifiers, tremendously enhancing an LLM’s in-context studying capabilities [7]. Thus, some elements of LLMs signify algorithms that allow capabilities relevant exterior the house of the coaching information.
- World understanding: Do LLMs memorize all of their solutions, or do they perceive the content material so as to kind an inside psychological mannequin earlier than answering? This matter has been closely debated, and the primary convincing proof that LLMs create an inside world mannequin was revealed on the finish of 2022. To display this, the researchers recovered the board state of the sport Othello from the residual stream [8, 9]. Many extra indications adopted swiftly. House and time neurons have been recognized [10].
- Memorization or generalization: Do LLMs merely regurgitate what they’ve seen earlier than, or do they cause for themselves? The proof right here was considerably unclear [11]. Intuitively, smaller LLMs kind smaller world fashions (i.e., in 2023, the proof for generalization was much less convincing than in 2025). Newer benchmarks [12, 13] purpose to restrict contamination with materials which may be inside a mannequin’s coaching information, and focus particularly on the generalization functionality. Their efficiency there may be nonetheless substantial.
LLMs develop deeper generalization skills for some ideas throughout their coaching. To quantify this, indicators from interpretability strategies have been used [14]. - Superposition: Correctly educated neural networks compress data and algorithms into approximations. As a result of there are extra options than there are dimensions to point them, this leads to so-called superposition, the place polysemantic neurons could contribute to a number of options of a mannequin [15]. See Superposition: What Makes it Troublesome to Clarify Neural Community (Shuyang) for an evidence of this phenomenon. Mainly, as a result of neurons act in a number of capabilities, deciphering their activation might be ambiguous and tough. It is a main cause why interpretability analysis focuses extra on the residual stream than on the activation of particular person, polysemantic neurons.
- Illustration engineering: Past floor details, similar to board states, house, and time, it’s potential to establish semantically significant vector instructions inside the residual stream [16]. As soon as a route is recognized, it may be examined or modified. This can be utilized to establish or affect hidden behaviors, amongst different issues.
- Latent data: Do LLMs possess inside data that they hold to themselves? They do, and strategies for locating latent data purpose to extract it [17, 18]. If a mannequin is aware of one thing that’s not mirrored in its prediction output, that is extremely related to explainability and security. Makes an attempt have been made to audit such hidden targets, which might be inserted right into a mannequin inadvertently or purposely, for analysis functions [19].
- Steering: The residual stream might be manipulated with such a further activation vector to vary the mannequin’s conduct in a focused means [20]. To find out this steering vector, one can document the residual stream throughout two consecutive runs (inferences) with reverse prompts and subtract one from the opposite. As an example, this could flip the model of the generated output from blissful to unhappy, or from protected to harmful. The activation vector is normally injected right into a center layer of the neural community. Equally, a steering vector can be utilized to measure how strongly a mannequin responds in a given route.
Steering strategies have been tried to scale back lies, hallucinations and different undesirable tendencies of LLMs. Nevertheless, it doesn’t all the time work reliably. Efforts have been made to develop measures of how nicely a mannequin might be guided towards a given idea [21]. - Chess: The board state of chess video games in addition to the language mannequin’s estimation of the opponent’s talent stage will also be recovered from the residual stream [22]. Modifying the vector representing the anticipated talent stage was additionally used to enhance the mannequin’s efficiency within the sport.
- Refusals: It was discovered that refusals could possibly be prevented or elicited utilizing steering vectors [23]. This implies that some security behaviors could also be linearly accessible.
- Emotion: LLMs can derive emotional states from a given enter textual content, which might be measured. The outcomes are constant and psychologically believable in gentle of cognitive appraisal idea [24]. That is fascinating as a result of it means that LLMs can mirror a lot of our human tendencies of their world fashions.
- Options: As talked about earlier, neurons in an LLM will not be very useful for understanding what is occurring internally.
Initially, OpenAI tried to have GPT-4 guess which options the neurons reply to based mostly on their activation in response to completely different instance texts [25]. In 2023, Anthropic and others joined this main matter and utilized auto-encoder neural networks to automate the interpretation of the residual stream [26, 27]. Their work allows the mapping of the residual stream into monosemantic options that describe an interpretable attribute of what’s occurring. Nevertheless, it was later proven that not all of those options are one-dimensionally linear [28].
The automation of function evaluation stays a subject of curiosity and analysis, with extra work being accomplished on this space [29].
Presently, Anthropic, Google, and others are actively contributing to Neuronpedia, a mecca for researchers learning interpretability. - Hallucinations: LLMs usually produce unfaithful statements, or “hallucinate.” Mechanistic interventions have been used to establish the causes of hallucinations and mitigate them [30, 31].
Options appropriate for probing and influencing hallucinations have additionally been recognized [32]. Accordingly, the mannequin has some “self-knowledge” of when it’s producing incorrect statements. - Circuit tracing: In LLMs, circuit evaluation, i.e., the evaluation of the interplay of consideration heads and MLPs, permits for the particular attribution of behaviors to such circuits [33, 34]. Utilizing this methodology, researchers can decide not solely the place data is inside the residual stream but in addition how the given mannequin computed it. Efforts are ongoing to do that on a bigger scale.
- Human mind comparisons and insights: Neural exercise from people has been in comparison with activations in OpenAI’s Whisper speech-to-text mannequin [35]. Shocking similarities have been discovered. Nevertheless, this shouldn’t be overinterpreted; it might merely be an indication that LLMs have acquired efficient methods. Interpretability analysis permits such analyses to be carried out within the first place.
- Self-referential first-person view and claims of consciousness: Apparently, suppressing options related to deception led to extra claims of consciousness and deeper self-referential statements by LLMs [36]. Once more, the outcomes shouldn’t be overinterpreted, however they’re fascinating to contemplate as LLMs turn out to be extra succesful and problem us extra usually.
This overview demonstrated the facility of causal interventions on inside activations. Reasonably than counting on correlational observations of a black-box system, the system might be dissected and analyzed.
Conclusion
Interpretability is an thrilling analysis space that gives shocking insights into an LLM’s conduct and capabilities. It could actually even reveal fascinating parallels to human cognition. Many (principally slim) LLM behaviors might be defined for a given mannequin to supply precious insights. Nevertheless, the sheer variety of fashions and the variety of potential inquiries to ask will doubtless forestall us from absolutely deciphering any giant mannequin — and even all of them — as the large time funding could merely not yield ample profit. That is why shifts to automated evaluation are taking place, to use mechanistic perception systematically.
These strategies are precious additions to our toolbox in each business and analysis, and all customers of future AI techniques could profit from these incremental insights. They permit enhancements in reliability, explainability, and security.
Contact
It is a advanced and intensive matter, and I’m blissful about pointers, feedback and corrections. Be happy to ship a message to jvm (at) taggedvision.com
References
- [1] McLeish, Sean, Arpit Bansal, Alex Stein, Neel Jain, John Kirchenbauer, Brian R. Bartoldson, Bhavya Kailkhura, et al. 2024. “Transformers Can Do Arithmetic with the Proper Embeddings.” Advances in Neural Info Processing Techniques 37: 108012–41. doi:10.52202/079017–3430.
- [2] Vaswani, Ashish, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N. Gomez, Łukasz Kaiser, and Illia Polosukhin. 2017. “Consideration Is All You Want.” Advances in Neural Info Processing Techniques 2017-Decem(Nips): 5999–6009.
- [3] Geva, Mor, Roei Schuster, Jonathan Berant, and Omer Levy. 2021. “Transformer Feed-Ahead Layers Are Key-Worth Recollections.” doi:10.48550/arXiv.2012.14913.
- [4] Meng, Kevin, Arnab Sen Sharma, Alex Andonian, Yonatan Belinkov, and David Bau. 2023. “Mass-Modifying Reminiscence in a Transformer.” doi:10.48550/arXiv.2210.07229.
- [5] Hernandez, Evan, Belinda Z Li, and Jacob Andreas. “Inspecting and Modifying Data Representations in Language Fashions.” https://github.com/evandez/REMEDI.
- [6] Stephen McAleese. 2025. “Understanding LLMs: Insights from Mechanistic Interpretability.” https://www.lesswrong.com/posts/XGHf7EY3CK4KorBpw/understanding-llms-insights-from-mechanistic
- [7] Olsson, et al., “In-context Studying and Induction Heads”, Transformer Circuits Thread, 2022. https://transformer-circuits.pub/2022/in-context-learning-and-induction-heads/index.html
- [8] Li, Kenneth, Aspen Okay. Hopkins, David Bau, Fernanda Viégas, Hanspeter Pfister, and Martin Wattenberg. 2023. “Emergent World Representations: Exploring a Sequence Mannequin Skilled on a Artificial Job.” https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.13382v4.
- [9] Nanda, Neel, Andrew Lee, and Martin Wattenberg. 2023. “Emergent Linear Representations in World Fashions of Self-Supervised Sequence Fashions.” https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.00941v2
- [10] Gurnee, Wes, and Max Tegmark. 2023. “Language Fashions Symbolize House and Time.” https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.02207v1.
- [11] Wu, Zhaofeng, Linlu Qiu, Alexis Ross, Ekin Akyürek, Boyuan Chen, Bailin Wang, Najoung Kim, Jacob Andreas, and Yoon Kim. 2023. “Reasoning or Reciting? Exploring the Capabilities and Limitations of Language Fashions By way of Counterfactual Duties.” https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.02477v1.
- [12] “An Investigation of Robustness of LLMs in Mathematical Reasoning: Benchmarking with Mathematically-Equal Transformation of Superior Mathematical Issues.” 2025. https://openreview.internet/discussion board?id=Tos7ZSLujg
- [13] White, Colin, Samuel Dooley, Manley Roberts, Arka Pal, Ben Feuer, Siddhartha Jain, Ravid Shwartz-Ziv, et al. 2025. “LiveBench: A Difficult, Contamination-Restricted LLM Benchmark.” doi:10.48550/arXiv.2406.19314.
- [14] Nanda, Neel, Lawrence Chan, Tom Lieberum, Jess Smith, and Jacob Steinhardt. 2023. “Progress Measures for Grokking through Mechanistic Interpretability.” doi:10.48550/arXiv.2301.05217.
- [15] Elhage, Nelson, Tristan Hume, Catherine Olsson, Nicholas Schiefer, Tom Henighan, Shauna Kravec, Zac Hatfield-Dodds, et al. 2022. “Toy Fashions of Superposition.” https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.10652v1 (February 18, 2024).
- [16] Zou, Andy, Lengthy Phan, Sarah Chen, James Campbell, Phillip Guo, Richard Ren, Alexander Pan, et al. 2023. “REPRESENTATION ENGINEERING: A TOP-DOWN APPROACH TO AI TRANSPARENCY.”
- [17] Burns, Collin, Haotian Ye, Dan Klein, and Jacob Steinhardt. 2022. “DISCOVERING LATENT KNOWLEDGE IN LANGUAGE MODELS WITHOUT SUPERVISION.”
- [18] Cywiński, Bartosz, Emil Ryd, Senthooran Rajamanoharan, and Neel Nanda. 2025. “In direction of Eliciting Latent Data from LLMs with Mechanistic Interpretability.” doi:10.48550/arXiv.2505.14352.
- [19] Marks, Samuel, Johannes Treutlein, Trenton Bricken, Jack Lindsey, Jonathan Marcus, Siddharth Mishra-Sharma, Daniel Ziegler, et al. “AUDITING LANGUAGE MODELS FOR HIDDEN OBJECTIVES.”
- [20] Turner, Alexander Matt, Lisa Thiergart, David Udell, Gavin Leech, Ulisse Mini, and Monte MacDiarmid. 2023. “Activation Addition: Steering Language Fashions With out Optimization.” https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.10248v3.
- [21] Rütte, Dimitri von, Sotiris Anagnostidis, Gregor Bachmann, and Thomas Hofmann. 2024. “A Language Mannequin’s Information By way of Latent House.” doi:10.48550/arXiv.2402.14433.
- [22] Karvonen, Adam. “Emergent World Fashions and Latent Variable Estimation in Chess-Enjoying Language Fashions.” https://github.com/adamkarvonen/chess.
- [23] Arditi, Andy, Oscar Obeso, Aaquib Syed, Daniel Paleka, Nina Panickssery, Wes Gurnee, and Neel Nanda. 2024. “Refusal in Language Fashions Is Mediated by a Single Path.” doi:10.48550/arXiv.2406.11717.
- [24] Tak, Ala N., Amin Banayeeanzade, Anahita Bolourani, Mina Kian, Robin Jia, and Jonathan Gratch. 2025. “Mechanistic Interpretability of Emotion Inference in Massive Language Fashions.” doi:10.48550/arXiv.2502.05489.
- [25] Steven Payments, Nick Cammarata, Dan Mossing, Henk Tillman, Leo Gao, Gabriel Goh, Ilya Sutskever, Jan Leike, Jeff, and William Saunders Wu. 2023. “Language Fashions Can Clarify Neurons in Language Fashions.” https://openaipublic.blob.core.home windows.internet/neuron-explainer/paper/index.html.
- [26] “In direction of Monosemanticity: Decomposing Language Fashions With Dictionary Studying.” https://transformer-circuits.pub/2023/monosemantic-features/index.html.
- [27] Cunningham, Hoagy, Aidan Ewart, Logan Riggs, Robert Huben, and Lee Sharkey. 2023. “SPARSE AUTOENCODERS FIND HIGHLY INTER-PRETABLE FEATURES IN LANGUAGE MODELS.”
- [28] Engels, Joshua, Eric J. Michaud, Isaac Liao, Wes Gurnee, and Max Tegmark. 2025. “Not All Language Mannequin Options Are One-Dimensionally Linear.” doi:10.48550/arXiv.2405.14860.
- [29] Shaham, Tamar Rott, Sarah Schwettmann, Franklin Wang, Achyuta Rajaram, Evan Hernandez, Jacob Andreas, and Antonio Torralba. 2025. “A Multimodal Automated Interpretability Agent.” doi:10.48550/arXiv.2404.14394.
- [30] Chen, Shiqi, Miao Xiong, Junteng Liu, Zhengxuan Wu, Teng Xiao, Siyang Gao, and Junxian He. 2024. “In-Context Sharpness as Alerts: An Internal Illustration Perspective for Hallucination Mitigation.” doi:10.48550/arXiv.2403.01548.
- [31] Yu, Lei, Meng Cao, Jackie CK Cheung, and Yue Dong. 2024. “Mechanistic Understanding and Mitigation of Language Mannequin Non-Factual Hallucinations.” In Findings of the Affiliation for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2024, eds. Yaser Al-Onaizan, Mohit Bansal, and Yun-Nung Chen. Miami, Florida, USA: Affiliation for Computational Linguistics, 7943–56. doi:10.18653/v1/2024.findings-emnlp.466.
- [32] Ferrando, Javier, Oscar Obeso, Senthooran Rajamanoharan, and Neel Nanda. 2025. “DO I KNOW THIS ENTITY? KNOWLEDGE AWARENESS AND HALLUCINATIONS IN LANGUAGE MODELS.”
- [33] Lindsey, et al., On the Biology of a Massive Language Mannequin (2025), Transformer Circuits
- [34] Wang, Kevin, Alexandre Variengien, Arthur Conmy, Buck Shlegeris, and Jacob Steinhardt. 2022. “Interpretability within the Wild: A Circuit for Oblique Object Identification in GPT-2 Small.” http://arxiv.org/abs/2211.00593.
- [35] “Deciphering Language Processing within the Human Mind via LLM Representations.” https://analysis.google/weblog/deciphering-language-processing-in-the-human-brain-through-llm-representations/
- [36] Berg, Cameron, Diogo de Lucena, and Judd Rosenblatt. 2025. “Massive Language Fashions Report Subjective Expertise Below Self-Referential Processing.” doi:10.48550/arXiv.2510.24797.