Right here’s the total code (written in JupyterLab). I’ll break down the code blocks within the following sections.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import geopandas as gpd
from geopy.distance import great_circle# SEC faculties with coordinates (coords by ChatGPT4):
information = {
'faculty': ['Alabama', 'LSU', 'Ole Miss', 'Miss State',
'Auburn', 'Arkansas', 'Missouri', 'Vanderbilt',
'Tennessee', 'Florida', 'Georgia', 'Kentucky',
'S. Carolina', 'TAMU', 'Texas', 'Oklahoma'],
'latitude': [33.209, 30.412, 34.365, 33.456,
32.603, 36.068, 38.951, 36.162,
35.960, 29.651, 33.950, 38.049,
34.000, 30.620, 30.284, 35.222],
'longitude': [-87.538, -91.177, -89.526, -88.811,
-85.484, -94.172, -92.328, -86.784,
-83.920, -82.324, -83.377, -84.500,
-81.034, -96.340, -97.740, -97.445]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(information)
# Choose a faculty to plot the gap from.
# Use the identical identify as within the earlier information dict:
SCHOOL = 'Texas'
# Set the grid decision.
# Bigger = larger res and smoother contours:
RESOLUTION = 500
# Get coordinates for SCHOOL:
school_index = df[df['school'] == SCHOOL].index[0]
school_coords = df.loc[school_index, ['latitude', 'longitude']].to_numpy()
# Create grid of factors for interpolation:
x_min, x_max = df['longitude'].min(), df['longitude'].max()
y_min, y_max = df['latitude'].min(), df['latitude'].max()
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min, x_max, RESOLUTION),
np.linspace(y_min, y_max, RESOLUTION))
# Calculate distances from SCHOOL to each level in grid:
distances = np.zeros(xx.form)
for i in vary(xx.form[0]):
for j in vary(xx.form[1]):
point_coords = (yy[i, j], xx[i, j])
distances[i, j] = great_circle(school_coords, point_coords).miles
# Create the color-filled contour map:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 8))
contour = ax.contourf(xx, yy, distances,
cmap='coolwarm',
alpha=0.9)
cbar = fig.colorbar(contour, ax=ax, shrink=0.7)
cbar.set_label(f'Distance from {SCHOOL} (miles)')
ax.scatter(df['longitude'], df['latitude'], s=2, shade='black')
# Load state boundaries from US Census Bureau:
url = 'https://www2.census.gov/geo/tiger/GENZ2021/shp/cb_2021_us_state_20m.zip'
states = gpd.read_file(url)
# Filter states throughout the map limits:
states = states.cx[x_min:x_max, y_min:y_max]
# Plot the state boundaries:
states.boundary.plot(ax=ax, linewidth=1, edgecolor='black')
# Add labels for the colleges:
for i, faculty in enumerate(df['school']):
ax.annotate(
faculty,
(df['longitude'][i], df['latitude'][i]),
textcoords="offset factors",
xytext=(2, 1),
ha='left',
fontsize=8
)
ax.set_xlabel('Longitude')
ax.set_ylabel('Latitude')
ax.set_title(f'Distance from {SCHOOL} to Different SEC Faculties')
# fig.savefig('distance_map.png', dpi=600)
plt.present()
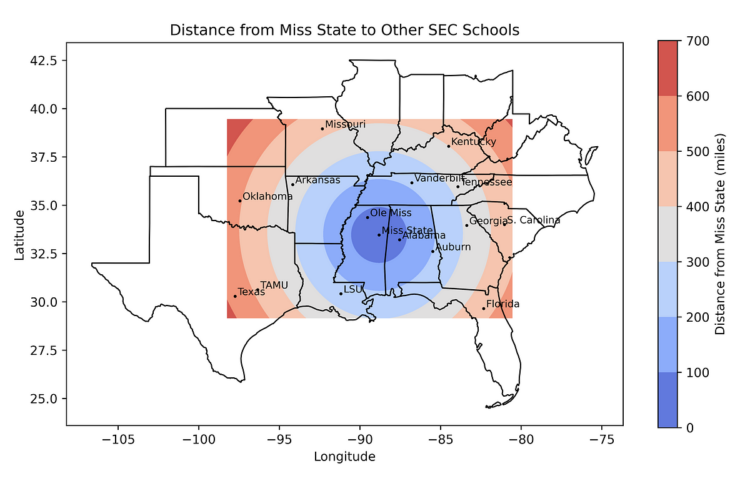
And right here’s the output, displaying the gap from the College of Texas in Austin to the opposite SEC faculties:
Importing Libraries
This mission requires NumPy, Matplotlib, pandas, geopandas, geopy, and scipy. You could find set up directions within the hyperlinks.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import geopandas as gpd
from geopy.distance import great_circle
Loading Knowledge
For the enter information, I made a listing of the colleges after which had ChatGPT produce the dictionary with the lat-lon coordinates. The dictionary was then transformed right into a pandas DataFrame named df.
# SEC faculties with coordinates (coords by ChatGPT4):
information = {
'faculty': ['Alabama', 'LSU', 'Ole Miss', 'Miss State',
'Auburn', 'Arkansas', 'Missouri', 'Vanderbilt',
'Tennessee', 'Florida', 'Georgia', 'Kentucky',
'S. Carolina', 'TAMU', 'Texas', 'Oklahoma'],
'latitude': [33.209, 30.412, 34.365, 33.456,
32.603, 36.068, 38.951, 36.162,
35.960, 29.651, 33.950, 38.049,
34.000, 30.620, 30.284, 35.222],
'longitude': [-87.538, -91.177, -89.526, -88.811,
-85.484, -94.172, -92.328, -86.784,
-83.920, -82.324, -83.377, -84.500,
-81.034, -96.340, -97.740, -97.445]
}df = pd.DataFrame(information)
Assigning Constants
The code will produce a distance map from one of many listed SEC faculties. We’ll assign the college’s identify (typed precisely because it seems within the dictionary) to a relentless named SCHOOL.
# Choose a faculty to plot the gap from.
# Use the identical identify as within the information dict:
SCHOOL = 'Texas'
To regulate the “smoothness” of the contours, we’ll use a relentless named RESOLUTION. The bigger the quantity, the finer the underlying grid and thus the smoother the contours. Values round 500–1,000 produce good outcomes.
# Set the grid decision.
# Bigger = larger res and smoother contours:
RESOLUTION = 500
Getting the Faculty Location
Now to get the desired faculty’s map coordinates. On this case, the college would be the College of Texas in Austin, Texas.
# Get coordinates for SCHOOL:
school_index = df[df['school'] == SCHOOL].index[0]
school_coords = df.loc[school_index, ['latitude', 'longitude']].to_numpy()
The primary line identifies the DataFrame index of the college specified by the SCHOOL fixed. This index is then used to get the college’s coordinates. As a result of index returns a listing of indices the place the situation is true, we use [0] to get the primary (presumably solely) merchandise on this record.
Subsequent, we extract latitude and longitude values from the DataFrame and convert them right into a NumPy array with the to_numpy() methodology.
In the event you’re unfamiliar with NumPy arrays, take a look at this text:
Creating the Grid
Earlier than we make a contour map, we should construct an everyday grid and populate the grid nodes (intersections) with distance values. The next code creates the grid.
# Create grid of factors for interpolation:
x_min, x_max = df['longitude'].min(), df['longitude'].max()
y_min, y_max = df['latitude'].min(), df['latitude'].max()
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min, x_max, RESOLUTION),
np.linspace(y_min, y_max, RESOLUTION))
Step one right here is to get the min and max values (x_min, x_max and y_min, y_max) of the longitude and latitude from the DataFrame.
Subsequent, we use NumPy’s meshgrid() methodology to create a grid of factors throughout the bounds outlined by the min and max latitudes and longitudes.
Right here’s how the grid seems to be for a decision of 100:
Every node will maintain a price that may be contoured.
Calculating Distances
The next code calculates concentric distances from the desired faculty.
# Calculate distances from SCHOOL to each level in grid:
distances = np.zeros(xx.form)
for i in vary(xx.form[0]):
for j in vary(xx.form[1]):
point_coords = (yy[i, j], xx[i, j])
distances[i, j] = great_circle(school_coords, point_coords).miles
The primary order of enterprise is to initialize a NumPy array referred to as distances. It has the identical form because thexx grid and is stuffed with zeroes. We’ll use it to retailer the calculated distances from SCHOOL.
Subsequent, we loop over the rows of the grid, then, in a nested loop, iterate over the columns of the grid. With every iteration we retrieve the coordinates of the purpose at place (i, j) within the grid, with yy and xx holding the grid coordinates.
The ultimate line calculates the great-circle distance (the gap between two factors on a sphere) from the college to the present level coordinates (point_coords). The last word result’s an array of distances with models in miles.
Creating the Map
Now that we’ve got x, y, and distance information, we are able to contour the gap values and make a show.
# Create the color-filled contour map:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 8))
contour = ax.contourf(xx, yy, distances,
cmap='coolwarm',
alpha=0.9)
cbar = fig.colorbar(contour, ax=ax, shrink=0.7)
cbar.set_label(f'Distance from {SCHOOL} (miles)')
ax.scatter(df['longitude'], df['latitude'], s=2, shade='black')
We begin by organising a Matplotlib determine of measurement 10 x 8. In the event you’re not accustomed to the fig, ax terminology, take a look at this terrific article for a fast introduction:
To attract the color-filled contours we use Matplotlib’s contourf() methodology. It makes use of the xx, yy, and distancesvalues, the coolwarm colormap, and a slight quantity of transparency (alpha=0.9).
The default shade bar for the show is missing, for my part, so we customise it considerably. The fig.colorbar() methodology provides a shade bar to the plot to point the gap scale. The shrink argument retains the peak of the colour bar from being disproportionate to the plot.
Lastly, we use Matplotlib’s scatter() methodology so as to add the college places to the map, with a marker measurement of 2. Later, we’ll label these factors with the college names.
Including the State Boundaries
The map at present has solely the college places to make use of as landmarks. To make the map extra relatable, the next code provides state boundaries.
# Load state boundaries from US Census Bureau:
url = 'https://www2.census.gov/geo/tiger/GENZ2021/shp/cb_2021_us_state_20m.zip'
states = gpd.read_file(url)# Filter states throughout the map limits:
states = states.cx[x_min:x_max, y_min:y_max]
# Plot the state boundaries:
states.boundary.plot(ax=ax, linewidth=1, edgecolor='black')
The third line makes use of geopandas’ cx indexer methodology for spatial slicing. It filters geometries in a GeoDataFrame primarily based on a bounding field outlined by the minimal and most x (longitude) and y (latitude) coordinates. Right here, we filter out all of the states exterior the bounding field.
Including Labels and a Title
The next code finishes the plot by tying up a number of unfastened ends, reminiscent of including the college names to their map markers, labeling the x and y axes, and setting an updateable title.
# Add labels for the colleges:
for i, faculty in enumerate(df['school']):
ax.annotate(
faculty,
(df['longitude'][i], df['latitude'][i]),
textcoords="offset factors",
xytext=(2, 1),
ha='left',
fontsize=8
)ax.set_xlabel('Longitude')
ax.set_ylabel('Latitude')
ax.set_title(f'Distance from {SCHOOL} to Different SEC Faculties')
fig.savefig('distance_map.png', dpi=600)
plt.present()
To label the colleges, we use a for loop and enumeration to decide on the proper coordinates and names for every faculty and use Matplotlib’s annotate() methodology to submit them on the map. We use annotate() fairly than the textual content() methodology to entry the xytext argument, which lets us shift the label to the place we wish it.