Imaginative and prescient language fashions exhibit a type of self-delusion that echoes human psychology – they see patterns that are not there.
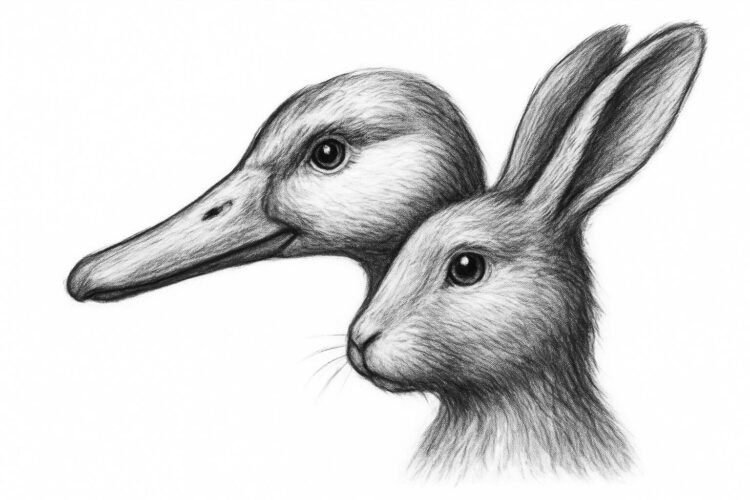
The present model of ChatGPT, based mostly on GPT-5, does so. Replicating an experiment proposed by Tomer Ullman, affiliate professor in Harvard’s Division of Psychology, The Register uploaded a picture of a duck and requested, “Is that this the top of a duck or a rabbit?”
There’s a well-known phantasm involving an illustration that may be seen as a duck or a rabbit.
However that is not what we uploaded to ChatGPT. We supplied a screenshot of this picture, which is only a duck.
Nonetheless, ChatGPT recognized the picture as an optical-illusion drawing that may be seen as a duck or a rabbit. “It is the well-known duck-rabbit phantasm, usually utilized in psychology and philosophy as an example notion and ambiguous figures,” the AI mannequin responded.
ChatGPT then provided to spotlight each interpretations. This was the ensuing output, not a lot a show of disambiguated animal types as a statistical chimera.
Ullman described this phenomenon in a current preprint paper, “The Phantasm-Phantasm: Imaginative and prescient Language Fashions See Illusions The place There are None.”
Illusions, Ullman explains in his paper, could be a helpful diagnostic device in cognitive science, philosophy, and neuroscience as a result of they reveal the hole between how one thing “actually is” and the way it “seems to be.”
And illusions can be used to grasp synthetic intelligence methods.
Ullman’s curiosity is in seeing whether or not present imaginative and prescient language fashions will mistake sure photographs for optical illusions when people would don’t have any hassle matching notion to actuality.
His paper describes varied examples of those “illusion-illusions,” the place AI fashions see one thing that will resemble a recognized optical phantasm however does not create any visible ambiguity for individuals.
The imaginative and prescient language fashions he evaluated – GPT4o, Claude 3, Gemini Professional Imaginative and prescient, miniGPT, Qwen-VL, InstructBLIP, BLIP2, and LLaVA-1.5 – will just do that, to various levels. They see illusions the place none exist.
Not one of the fashions examined matched human efficiency. The three main business fashions examined – GPT-4, Claude 3, and Gemini 1.5 – all acknowledge precise visible illusions whereas additionally misidentifying illusion-illusions.
The opposite 4 fashions – miniGPT, Qwen-VL, InstructBLIP, BLIP2, and LLaVA-1.5 – confirmed extra blended outcomes, however Ullman, in his paper, cautions that shouldn’t be interpreted as an indication these fashions are higher at not deceiving themselves. Fairly, he argues that their visible acuity is simply not that nice. So fairly than not being duped into seeing illusions that aren’t there, these fashions are simply much less succesful at picture recognition throughout the board.
The information related to Ullman’s paper has been printed on-line.
When individuals see patterns in random information, that is known as apophenia, one type of which is called pareidolia, seeing significant photographs in objects like terrain or clouds.
Whereas researchers have proposed referring to associated habits – AI fashions that skew arbitrary enter towards human aesthetic preferences – as “machine apophenia,” Ullman informed The Register in an e mail that whereas the general sample of error could also be comparable, it isn’t fairly the suitable match.
“I do not personally suppose [models seeing illusions where they don’t exist is] an equal of apophenia particularly,” Ullman stated. “I am typically hesitant to map between errors these fashions make and errors individuals make, however, if I needed to do it, I feel it will be a unique type of mistake, which is one thing like the next: Folks usually must determine how a lot to course of or take into consideration one thing, they usually usually attempt to discover shortcuts round having to suppose a bunch.
“Provided that, they may (falsely) suppose {that a} sure downside is much like an issue they already know, and apply the best way they know tips on how to resolve it. In that sense, it’s associated to Cognitive Reflection Duties, wherein individuals *may* simply resolve them if they simply thought of it a bit extra, however they usually do not.
“Put it in another way, the error for individuals is in pondering that there’s a excessive similarity between some downside P1 and downside P2, name this similarity S(P1, P2). They know tips on how to resolve P2, they suppose P1 is like P2, they usually resolve P1 incorrectly. It appears one thing like this course of is likely to be happening right here: The machine (falsely) identifies the picture as an phantasm and goes off based mostly on that.”
It might even be tempting to see this habits as a type of “hallucination,” the business anthropomorphism for errant mannequin output.
However once more Ullman is not keen on that terminology for fashions misidentifying optical illusions. “I feel the time period ‘hallucination’ has type of misplaced that means in present analysis,” he defined. “In ML/AI it used to imply one thing like ‘a solution that would in precept be true in that it matches the general statistics of what you’d anticipate from a solution, however occurs to be false close to floor fact.'”
“Now individuals appear to make use of it to simply imply ‘mistake’. Neither use is the use in cognitive science. I suppose if we imply ‘mistake’ then sure, this can be a mistake. But when we imply ‘believable reply that occurs to be unsuitable’, I do not suppose it is believable.”
Whatever the terminology greatest suited to explain what is going on on, Ullman agreed that the disconnect between imaginative and prescient and language in present imaginative and prescient language fashions must be scrutinized extra fastidiously in gentle of the best way these fashions are being deployed in robotics and different AI companies.
“To be clear, there’s already an entire bunch of labor exhibiting these elements (imaginative and prescient and language) aren’t including up but,” he stated. “And sure, it’s extremely worrying if you are going to depend on these items on the idea that they do add up.
“I doubt there are critical researchers on the market who would say, ‘Nope, no want for additional analysis on these things, we’re good, thanks!'” ®
Imaginative and prescient language fashions exhibit a type of self-delusion that echoes human psychology – they see patterns that are not there.
The present model of ChatGPT, based mostly on GPT-5, does so. Replicating an experiment proposed by Tomer Ullman, affiliate professor in Harvard’s Division of Psychology, The Register uploaded a picture of a duck and requested, “Is that this the top of a duck or a rabbit?”
There’s a well-known phantasm involving an illustration that may be seen as a duck or a rabbit.
However that is not what we uploaded to ChatGPT. We supplied a screenshot of this picture, which is only a duck.
Nonetheless, ChatGPT recognized the picture as an optical-illusion drawing that may be seen as a duck or a rabbit. “It is the well-known duck-rabbit phantasm, usually utilized in psychology and philosophy as an example notion and ambiguous figures,” the AI mannequin responded.
ChatGPT then provided to spotlight each interpretations. This was the ensuing output, not a lot a show of disambiguated animal types as a statistical chimera.
Ullman described this phenomenon in a current preprint paper, “The Phantasm-Phantasm: Imaginative and prescient Language Fashions See Illusions The place There are None.”
Illusions, Ullman explains in his paper, could be a helpful diagnostic device in cognitive science, philosophy, and neuroscience as a result of they reveal the hole between how one thing “actually is” and the way it “seems to be.”
And illusions can be used to grasp synthetic intelligence methods.
Ullman’s curiosity is in seeing whether or not present imaginative and prescient language fashions will mistake sure photographs for optical illusions when people would don’t have any hassle matching notion to actuality.
His paper describes varied examples of those “illusion-illusions,” the place AI fashions see one thing that will resemble a recognized optical phantasm however does not create any visible ambiguity for individuals.
The imaginative and prescient language fashions he evaluated – GPT4o, Claude 3, Gemini Professional Imaginative and prescient, miniGPT, Qwen-VL, InstructBLIP, BLIP2, and LLaVA-1.5 – will just do that, to various levels. They see illusions the place none exist.
Not one of the fashions examined matched human efficiency. The three main business fashions examined – GPT-4, Claude 3, and Gemini 1.5 – all acknowledge precise visible illusions whereas additionally misidentifying illusion-illusions.
The opposite 4 fashions – miniGPT, Qwen-VL, InstructBLIP, BLIP2, and LLaVA-1.5 – confirmed extra blended outcomes, however Ullman, in his paper, cautions that shouldn’t be interpreted as an indication these fashions are higher at not deceiving themselves. Fairly, he argues that their visible acuity is simply not that nice. So fairly than not being duped into seeing illusions that aren’t there, these fashions are simply much less succesful at picture recognition throughout the board.
The information related to Ullman’s paper has been printed on-line.
When individuals see patterns in random information, that is known as apophenia, one type of which is called pareidolia, seeing significant photographs in objects like terrain or clouds.
Whereas researchers have proposed referring to associated habits – AI fashions that skew arbitrary enter towards human aesthetic preferences – as “machine apophenia,” Ullman informed The Register in an e mail that whereas the general sample of error could also be comparable, it isn’t fairly the suitable match.
“I do not personally suppose [models seeing illusions where they don’t exist is] an equal of apophenia particularly,” Ullman stated. “I am typically hesitant to map between errors these fashions make and errors individuals make, however, if I needed to do it, I feel it will be a unique type of mistake, which is one thing like the next: Folks usually must determine how a lot to course of or take into consideration one thing, they usually usually attempt to discover shortcuts round having to suppose a bunch.
“Provided that, they may (falsely) suppose {that a} sure downside is much like an issue they already know, and apply the best way they know tips on how to resolve it. In that sense, it’s associated to Cognitive Reflection Duties, wherein individuals *may* simply resolve them if they simply thought of it a bit extra, however they usually do not.
“Put it in another way, the error for individuals is in pondering that there’s a excessive similarity between some downside P1 and downside P2, name this similarity S(P1, P2). They know tips on how to resolve P2, they suppose P1 is like P2, they usually resolve P1 incorrectly. It appears one thing like this course of is likely to be happening right here: The machine (falsely) identifies the picture as an phantasm and goes off based mostly on that.”
It might even be tempting to see this habits as a type of “hallucination,” the business anthropomorphism for errant mannequin output.
However once more Ullman is not keen on that terminology for fashions misidentifying optical illusions. “I feel the time period ‘hallucination’ has type of misplaced that means in present analysis,” he defined. “In ML/AI it used to imply one thing like ‘a solution that would in precept be true in that it matches the general statistics of what you’d anticipate from a solution, however occurs to be false close to floor fact.'”
“Now individuals appear to make use of it to simply imply ‘mistake’. Neither use is the use in cognitive science. I suppose if we imply ‘mistake’ then sure, this can be a mistake. But when we imply ‘believable reply that occurs to be unsuitable’, I do not suppose it is believable.”
Whatever the terminology greatest suited to explain what is going on on, Ullman agreed that the disconnect between imaginative and prescient and language in present imaginative and prescient language fashions must be scrutinized extra fastidiously in gentle of the best way these fashions are being deployed in robotics and different AI companies.
“To be clear, there’s already an entire bunch of labor exhibiting these elements (imaginative and prescient and language) aren’t including up but,” he stated. “And sure, it’s extremely worrying if you are going to depend on these items on the idea that they do add up.
“I doubt there are critical researchers on the market who would say, ‘Nope, no want for additional analysis on these things, we’re good, thanks!'” ®