says that “any sufficiently superior expertise is indistinguishable from magic”. That’s precisely how loads of at present’s AI frameworks really feel. Instruments like GitHub Copilot, Claude Desktop, OpenAI Operator, and Perplexity Comet are automating on a regular basis duties that might’ve appeared inconceivable to automate simply 5 years in the past. What’s much more outstanding is that with just some strains of code, we will construct our personal subtle AI instruments: ones that search by means of information, browse the net, click on hyperlinks, and even make purchases. It actually does really feel like magic.
Though I genuinely consider in knowledge wizards, I don’t consider in magic. I discover it thrilling (and sometimes useful) to grasp how issues are literally constructed and what’s occurring below the hood. That’s why I’ve determined to share a sequence of posts on agentic AI design ideas that’ll allow you to perceive how all these magical instruments really work.
To achieve a deep understanding, we’ll construct a multi-AI agent system from scratch. We’ll keep away from utilizing frameworks like CrewAI or smolagents and as a substitute work immediately with the inspiration mannequin API. Alongside the best way, we’ll discover the elemental agentic design patterns: reflection, software use, planning, and multi-agent setups. Then, we’ll mix all this information to construct a multi-AI agent system that may reply complicated data-related questions.
As Richard Feynman put it, “What I can not create, I don’t perceive.” So let’s begin constructing! On this article, we’ll give attention to the reflection design sample. However first, let’s determine what precisely reflection is.
What reflection is
Let’s mirror on how we (people) often work on duties. Think about I have to share the outcomes of a latest characteristic launch with my PM. I’ll probably put collectively a fast draft after which learn it a couple of times from starting to finish, guaranteeing that each one elements are constant, there’s sufficient info, and there are not any typos.
Or let’s take one other instance: writing a SQL question. I’ll both write it step-by-step, checking the intermediate outcomes alongside the best way, or (if it’s easy sufficient) I’ll draft it unexpectedly, execute it, take a look at the consequence (checking for errors or whether or not the consequence matches my expectations), after which tweak the question primarily based on that suggestions. I would rerun it, verify the consequence, and iterate till it’s proper.
So we hardly ever write lengthy texts from prime to backside in a single go. We often circle again, assessment, and tweak as we go. These suggestions loops are what assist us enhance the standard of our work.

LLMs use a distinct strategy. When you ask an LLM a query, by default, it’s going to generate a solution token by token, and the LLM received’t be capable to assessment its consequence and repair any points. However in an agentic AI setup, we will create suggestions loops for LLMs too, both by asking the LLM to assessment and enhance its personal reply or by sharing exterior suggestions with it (just like the outcomes of a SQL execution). And that’s the entire level of reflection. It sounds fairly easy, however it will probably yield considerably higher outcomes.
There’s a considerable physique of analysis exhibiting the advantages of reflection:

- In “Reflexion: Language Brokers with Verbal Reinforcement Studying” Shinn et al. (2023), the authors achieved a 91% move@1 accuracy on the HumanEval coding benchmark, surpassing the earlier state-of-the-art GPT-4, which scored simply 80%. Additionally they discovered that Reflexion considerably outperforms all baseline approaches on the HotPotQA benchmark (a Wikipedia-based Q&A dataset that challenges brokers to parse content material and cause over a number of supporting paperwork).

Reflection is very impactful in agentic methods as a result of it may be used to course-correct at many steps of the method:
- When a person asks a query, the LLM can use reflection to guage whether or not the request is possible.
- When the LLM places collectively an preliminary plan, it will probably use reflection to double-check whether or not the plan is sensible and will help obtain the purpose.
- After every execution step or software name, the agent can consider whether or not it’s on monitor and whether or not it’s value adjusting the plan.
- When the plan is totally executed, the agent can mirror to see whether or not it has really completed the purpose and solved the duty.
It’s clear that reflection can considerably enhance accuracy. Nonetheless, there are trade-offs value discussing. Reflection may require a number of further calls to the LLM and doubtlessly different methods, which might result in elevated latency and prices. So in enterprise circumstances, it’s value contemplating whether or not the standard enhancements justify the bills and delays within the person move.
Reflection in frameworks
Since there’s little doubt that reflection brings worth to AI brokers, it’s broadly utilized in common frameworks. Let’s take a look at some examples.
The concept of reflection was first proposed within the paper “ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Appearing in Language Fashions” by Yao et al. (2022). ReAct is a framework that mixes interleaving levels of Reasoning (reflection by means of specific thought traces) and Appearing (task-relevant actions in an setting). On this framework, reasoning guides the selection of actions, and actions produce new observations that inform additional reasoning. The reasoning stage itself is a mixture of reflection and planning.
This framework grew to become fairly common, so there are actually a number of off-the-shelf implementations, comparable to:
- The DSPy framework by Databricks has a
ReActclass, - In LangGraph, you should utilize the
create_react_agentperform, - Code brokers within the smolagents library by HuggingFace are additionally primarily based on the ReAct structure.
Reflection from scratch
Now that we’ve realized the speculation and explored current implementations, it’s time to get our palms soiled and construct one thing ourselves. Within the ReAct strategy, brokers use reflection at every step, combining planning with reflection. Nonetheless, to grasp the influence of reflection extra clearly, we’ll take a look at it in isolation.
For example, we’ll use text-to-SQL: we’ll give an LLM a query and count on it to return a sound SQL question. We’ll be working with a flight delay dataset and the ClickHouse SQL dialect.
We’ll begin through the use of direct technology with none reflection as our baseline. Then, we’ll strive utilizing reflection by asking the mannequin to critique and enhance the SQL, or by offering it with further suggestions. After that, we’ll measure the standard of our solutions to see whether or not reflection really results in higher outcomes.
Direct technology
We’ll start with essentially the most easy strategy, direct technology, the place we ask the LLM to generate SQL that solutions a person question.
pip set up anthropicWe have to specify the API Key for the Anthropic API.
import os
os.environ['ANTHROPIC_API_KEY'] = config['ANTHROPIC_API_KEY']The following step is to initialise the shopper, and we’re all set.
import anthropic
shopper = anthropic.Anthropic()Now we will use this shopper to ship messages to the LLM. Let’s put collectively a perform to generate SQL primarily based on a person question. I’ve specified the system immediate with primary directions and detailed details about the info schema. I’ve additionally created a perform to ship the system immediate and person question to the LLM.
base_sql_system_prompt = '''
You're a senior SQL developer and your activity is to assist generate a SQL question primarily based on person necessities.
You're working with ClickHouse database. Specify the format (Tab Separated With Names) within the SQL question output to make sure that column names are included within the output.
Don't use depend(*) in your queries since it is a dangerous follow with columnar databases, choose utilizing depend().
Be certain that the question is syntactically appropriate and optimized for efficiency, bearing in mind ClickHouse particular options (i.e. that ClickHouse is a columnar database and helps features like ARRAY JOIN, SAMPLE, and so forth.).
Return solely the SQL question with none further explanations or feedback.
You can be working with flight_data desk which has the next schema:
Column Title | Information Sort | Null % | Instance Worth | Description
--- | --- | --- | --- | ---
yr | Int64 | 0.0 | 2024 | 12 months of flight
month | Int64 | 0.0 | 1 | Month of flight (1–12)
day_of_month | Int64 | 0.0 | 1 | Day of the month
day_of_week | Int64 | 0.0 | 1 | Day of week (1=Monday … 7=Sunday)
fl_date | datetime64[ns] | 0.0 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | Flight date (YYYY-MM-DD)
op_unique_carrier | object | 0.0 | 9E | Distinctive provider code
op_carrier_fl_num | float64 | 0.0 | 4814.0 | Flight quantity for reporting airline
origin | object | 0.0 | JFK | Origin airport code
origin_city_name | object | 0.0 | "New York, NY" | Origin metropolis title
origin_state_nm | object | 0.0 | New York | Origin state title
dest | object | 0.0 | DTW | Vacation spot airport code
dest_city_name | object | 0.0 | "Detroit, MI" | Vacation spot metropolis title
dest_state_nm | object | 0.0 | Michigan | Vacation spot state title
crs_dep_time | Int64 | 0.0 | 1252 | Scheduled departure time (native, hhmm)
dep_time | float64 | 1.31 | 1247.0 | Precise departure time (native, hhmm)
dep_delay | float64 | 1.31 | -5.0 | Departure delay in minutes (unfavorable if early)
taxi_out | float64 | 1.35 | 31.0 | Taxi out time in minutes
wheels_off | float64 | 1.35 | 1318.0 | Wheels-off time (native, hhmm)
wheels_on | float64 | 1.38 | 1442.0 | Wheels-on time (native, hhmm)
taxi_in | float64 | 1.38 | 7.0 | Taxi in time in minutes
crs_arr_time | Int64 | 0.0 | 1508 | Scheduled arrival time (native, hhmm)
arr_time | float64 | 1.38 | 1449.0 | Precise arrival time (native, hhmm)
arr_delay | float64 | 1.61 | -19.0 | Arrival delay in minutes (unfavorable if early)
cancelled | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Cancelled flight indicator (0=No, 1=Sure)
cancellation_code | object | 98.64 | B | Cause for cancellation (if cancelled)
diverted | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Diverted flight indicator (0=No, 1=Sure)
crs_elapsed_time | float64 | 0.0 | 136.0 | Scheduled elapsed time in minutes
actual_elapsed_time | float64 | 1.61 | 122.0 | Precise elapsed time in minutes
air_time | float64 | 1.61 | 84.0 | Flight time in minutes
distance | float64 | 0.0 | 509.0 | Distance between origin and vacation spot (miles)
carrier_delay | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Provider-related delay in minutes
weather_delay | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Climate-related delay in minutes
nas_delay | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Nationwide Air System delay in minutes
security_delay | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Safety delay in minutes
late_aircraft_delay | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Late plane delay in minutes
'''
def generate_direct_sql(rec):
# making an LLM name
message = shopper.messages.create(
mannequin = "claude-3-5-haiku-latest",
# I selected smaller mannequin in order that it is simpler for us to see the influence
max_tokens = 8192,
system=base_sql_system_prompt,
messages = [
{'role': 'user', 'content': rec['question']}
]
)
sql = message.content material[0].textual content
# cleansing the output
if sql.endswith('```'):
sql = sql[:-3]
if sql.startswith('```sql'):
sql = sql[6:]
return sqlThat’s it. Now let’s check our text-to-SQL answer. I’ve created a small analysis set of 20 question-and-answer pairs that we will use to verify whether or not our system is working properly. Right here’s one instance:
{
'query': 'What was the best velocity in mph?',
'reply': '''
choose max(distance / (air_time / 60)) as max_speed
from flight_data
the place air_time > 0
format TabSeparatedWithNames'''
}Let’s use our text-to-SQL perform to generate SQL for all person queries within the check set.
# load analysis set
with open('./knowledge/flight_data_qa_pairs.json', 'r') as f:
qa_pairs = json.load(f)
qa_pairs_df = pd.DataFrame(qa_pairs)
tmp = []
# executing LLM for every query in our eval set
for rec in tqdm.tqdm(qa_pairs_df.to_dict('data')):
llm_sql = generate_direct_sql(rec)
tmp.append(
{
'id': rec['id'],
'llm_direct_sql': llm_sql
}
)
llm_direct_df = pd.DataFrame(tmp)
direct_result_df = qa_pairs_df.merge(llm_direct_df, on = 'id')Now we now have our solutions, and the subsequent step is to measure the standard.
Measuring high quality
Sadly, there’s no single appropriate reply on this scenario, so we will’t simply evaluate the SQL generated by the LLM to a reference reply. We have to provide you with a option to measure high quality.
There are some elements of high quality that we will verify with goal standards, however to verify whether or not the LLM returned the correct reply, we’ll want to make use of an LLM. So I’ll use a mixture of approaches:
- First, we’ll use goal standards to verify whether or not the proper format was specified within the SQL (we instructed the LLM to make use of
TabSeparatedWithNames). - Second, we will execute the generated question and see whether or not ClickHouse returns an execution error.
- Lastly, we will create an LLM choose that compares the output from the generated question to our reference reply and checks whether or not they differ.
Let’s begin by executing the SQL. It’s value noting that our get_clickhouse_data perform doesn’t throw an exception. As a substitute, it returns textual content explaining the error, which may be dealt with by the LLM later.
CH_HOST = 'http://localhost:8123' # default handle
import requests
import pandas as pd
import tqdm
# perform to execute SQL question
def get_clickhouse_data(question, host = CH_HOST, connection_timeout = 1500):
r = requests.submit(host, params = {'question': question},
timeout = connection_timeout)
if r.status_code == 200:
return r.textual content
else:
return 'Database returned the next error:n' + r.textual content
# getting the outcomes of SQL execution
direct_result_df['llm_direct_output'] = direct_result_df['llm_direct_sql'].apply(get_clickhouse_data)
direct_result_df['answer_output'] = direct_result_df['answer'].apply(get_clickhouse_data)The following step is to create an LLM choose. For this, I’m utilizing a series‑of‑thought strategy that prompts the LLM to offer its reasoning earlier than giving the ultimate reply. This provides the mannequin time to suppose by means of the issue, which improves response high quality.
llm_judge_system_prompt = '''
You're a senior analyst and your activity is to match two SQL question outcomes and decide if they're equal.
Focus solely on the info returned by the queries, ignoring any formatting variations.
Take note of the preliminary person question and data wanted to reply it. For instance, if person requested for the typical distance, and each queries return the identical common worth however in one among them there's additionally a depend of data, it is best to take into account them equal, since each present the identical requested info.
Reply with a JSON of the next construction:
{
'reasoning': '',
'equivalence':
}
Be certain that ONLY JSON is within the output.
You can be working with flight_data desk which has the next schema:
Column Title | Information Sort | Null % | Instance Worth | Description
--- | --- | --- | --- | ---
yr | Int64 | 0.0 | 2024 | 12 months of flight
month | Int64 | 0.0 | 1 | Month of flight (1–12)
day_of_month | Int64 | 0.0 | 1 | Day of the month
day_of_week | Int64 | 0.0 | 1 | Day of week (1=Monday … 7=Sunday)
fl_date | datetime64[ns] | 0.0 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | Flight date (YYYY-MM-DD)
op_unique_carrier | object | 0.0 | 9E | Distinctive provider code
op_carrier_fl_num | float64 | 0.0 | 4814.0 | Flight quantity for reporting airline
origin | object | 0.0 | JFK | Origin airport code
origin_city_name | object | 0.0 | "New York, NY" | Origin metropolis title
origin_state_nm | object | 0.0 | New York | Origin state title
dest | object | 0.0 | DTW | Vacation spot airport code
dest_city_name | object | 0.0 | "Detroit, MI" | Vacation spot metropolis title
dest_state_nm | object | 0.0 | Michigan | Vacation spot state title
crs_dep_time | Int64 | 0.0 | 1252 | Scheduled departure time (native, hhmm)
dep_time | float64 | 1.31 | 1247.0 | Precise departure time (native, hhmm)
dep_delay | float64 | 1.31 | -5.0 | Departure delay in minutes (unfavorable if early)
taxi_out | float64 | 1.35 | 31.0 | Taxi out time in minutes
wheels_off | float64 | 1.35 | 1318.0 | Wheels-off time (native, hhmm)
wheels_on | float64 | 1.38 | 1442.0 | Wheels-on time (native, hhmm)
taxi_in | float64 | 1.38 | 7.0 | Taxi in time in minutes
crs_arr_time | Int64 | 0.0 | 1508 | Scheduled arrival time (native, hhmm)
arr_time | float64 | 1.38 | 1449.0 | Precise arrival time (native, hhmm)
arr_delay | float64 | 1.61 | -19.0 | Arrival delay in minutes (unfavorable if early)
cancelled | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Cancelled flight indicator (0=No, 1=Sure)
cancellation_code | object | 98.64 | B | Cause for cancellation (if cancelled)
diverted | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Diverted flight indicator (0=No, 1=Sure)
crs_elapsed_time | float64 | 0.0 | 136.0 | Scheduled elapsed time in minutes
actual_elapsed_time | float64 | 1.61 | 122.0 | Precise elapsed time in minutes
air_time | float64 | 1.61 | 84.0 | Flight time in minutes
distance | float64 | 0.0 | 509.0 | Distance between origin and vacation spot (miles)
carrier_delay | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Provider-related delay in minutes
weather_delay | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Climate-related delay in minutes
nas_delay | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Nationwide Air System delay in minutes
security_delay | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Safety delay in minutes
late_aircraft_delay | int64 | 0.0 | 0 | Late plane delay in minutes
'''
llm_judge_user_prompt_template = '''
Right here is the preliminary person question:
{user_query}
Right here is the SQL question generated by the primary analyst:
SQL:
{sql1}
Database output:
{result1}
Right here is the SQL question generated by the second analyst:
SQL:
{sql2}
Database output:
{result2}
'''
def llm_judge(rec, field_to_check):
# assemble the person immediate
user_prompt = llm_judge_user_prompt_template.format(
user_query = rec['question'],
sql1 = rec['answer'],
result1 = rec['answer_output'],
sql2 = rec[field_to_check + '_sql'],
result2 = rec[field_to_check + '_output']
)
# make an LLM name
message = shopper.messages.create(
mannequin = "claude-sonnet-4-5",
max_tokens = 8192,
temperature = 0.1,
system = llm_judge_system_prompt,
messages=[
{'role': 'user', 'content': user_prompt}
]
)
knowledge = message.content material[0].textual content
# Strip markdown code blocks
knowledge = knowledge.strip()
if knowledge.startswith('```json'):
knowledge = knowledge[7:]
elif knowledge.startswith('```'):
knowledge = knowledge[3:]
if knowledge.endswith('```'):
knowledge = knowledge[:-3]
knowledge = knowledge.strip()
return json.hundreds(knowledge) Now, let’s run the LLM choose to get the outcomes.
tmp = []
for rec in tqdm.tqdm(direct_result_df.to_dict('data')):
strive:
judgment = llm_judge(rec, 'llm_direct')
besides Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing report {rec['id']}: {e}")
proceed
tmp.append(
{
'id': rec['id'],
'llm_judge_reasoning': judgment['reasoning'],
'llm_judge_equivalence': judgment['equivalence']
}
)
judge_df = pd.DataFrame(tmp)
direct_result_df = direct_result_df.merge(judge_df, on = 'id')Let’s take a look at one instance to see how the LLM choose works.
# person question
In 2024, what share of time all airplanes spent within the air?
# appropriate reply
choose (sum(air_time) / sum(actual_elapsed_time)) * 100 as percentage_in_air
the place yr = 2024
from flight_data
format TabSeparatedWithNames
percentage_in_air
81.43582596894757
# generated by LLM reply
SELECT
spherical(sum(air_time) / (sum(air_time) + sum(taxi_out) + sum(taxi_in)) * 100, 2) as air_time_percentage
FROM flight_data
WHERE yr = 2024
FORMAT TabSeparatedWithNames
air_time_percentage
81.39
# LLM choose response
{
'reasoning': 'Each queries calculate the proportion of time airplanes
spent within the air, however use completely different denominators. The primary question
makes use of actual_elapsed_time (which incorporates air_time + taxi_out + taxi_in
+ any floor delays), whereas the second makes use of solely (air_time + taxi_out
+ taxi_in). The second question is strategy is extra correct for answering
"time airplanes spent within the air" because it excludes floor delays.
Nonetheless, the outcomes are very shut (81.44% vs 81.39%), suggesting minimal
influence. These are materially completely different approaches that occur to yield
comparable outcomes',
'equivalence': FALSE
}The reasoning is sensible, so we will belief our choose. Now, let’s verify all LLM-generated queries.
def get_llm_accuracy(sql, output, equivalence):
issues = []
if 'format tabseparatedwithnames' not in sql.decrease():
issues.append('No format laid out in SQL')
if 'Database returned the next error' in output:
issues.append('SQL execution error')
if not equivalence and ('SQL execution error' not in issues):
issues.append('Incorrect reply supplied')
if len(issues) == 0:
return 'No issues detected'
else:
return ' + '.be a part of(issues)
direct_result_df['llm_direct_sql_quality_heuristics'] = direct_result_df.apply(
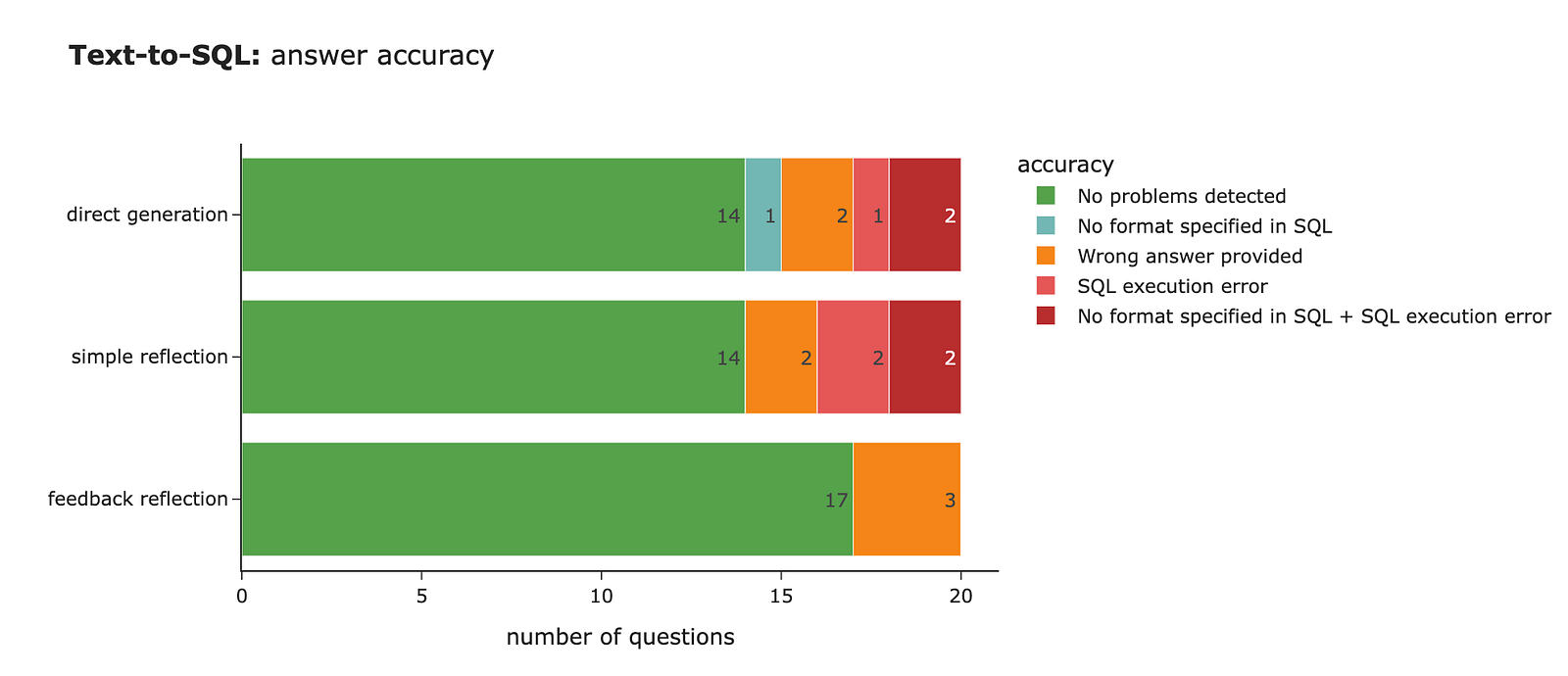
lambda row: get_llm_accuracy(row['llm_direct_sql'], row['llm_direct_output'], row['llm_judge_equivalence']), axis=1)The LLM returned the proper reply in 70% of circumstances, which isn’t dangerous. However there’s undoubtedly room for enchancment, because it usually both gives the fallacious reply or fails to specify the format accurately (typically inflicting SQL execution errors).

Including a mirrored image step
To enhance the standard of our answer, let’s strive including a mirrored image step the place we ask the mannequin to assessment and refine its reply.
For a mirrored image name, I’ll maintain the identical system immediate because it accommodates all the required details about SQL and the info schema. However I’ll tweak the person message to share the preliminary person question and the generated SQL, asking the LLM to critique and enhance it.
simple_reflection_user_prompt_template = '''
Your activity is to evaluate the SQL question generated by one other analyst and suggest enhancements if needed.
Examine whether or not the question is syntactically appropriate and optimized for efficiency.
Take note of nuances in knowledge (particularly time stamps varieties, whether or not to make use of complete elapsed time or time within the air, and so forth).
Be certain that the question solutions the preliminary person query precisely.
Because the consequence return the next JSON:
{{
'reasoning': '',
'refined_sql': ''
}}
Be certain that ONLY JSON is within the output and nothing else. Be certain that the output JSON is legitimate.
Right here is the preliminary person question:
{user_query}
Right here is the SQL question generated by one other analyst:
{sql}
'''
def simple_reflection(rec) -> str:
# establishing a person immediate
user_prompt = simple_reflection_user_prompt_template.format(
user_query=rec['question'],
sql=rec['llm_direct_sql']
)
# making an LLM name
message = shopper.messages.create(
mannequin="claude-3-5-haiku-latest",
max_tokens = 8192,
system=base_sql_system_prompt,
messages=[
{'role': 'user', 'content': user_prompt}
]
)
knowledge = message.content material[0].textual content
# strip markdown code blocks
knowledge = knowledge.strip()
if knowledge.startswith('```json'):
knowledge = knowledge[7:]
elif knowledge.startswith('```'):
knowledge = knowledge[3:]
if knowledge.endswith('```'):
knowledge = knowledge[:-3]
knowledge = knowledge.strip()
return json.hundreds(knowledge.substitute('n', ' ')) Let’s refine the queries with reflection and measure the accuracy. We don’t see a lot enchancment within the remaining high quality. We’re nonetheless at 70% appropriate solutions.

Let’s take a look at particular examples to grasp what occurred. First, there are a few circumstances the place the LLM managed to repair the issue, both by correcting the format or by including lacking logic to deal with zero values.
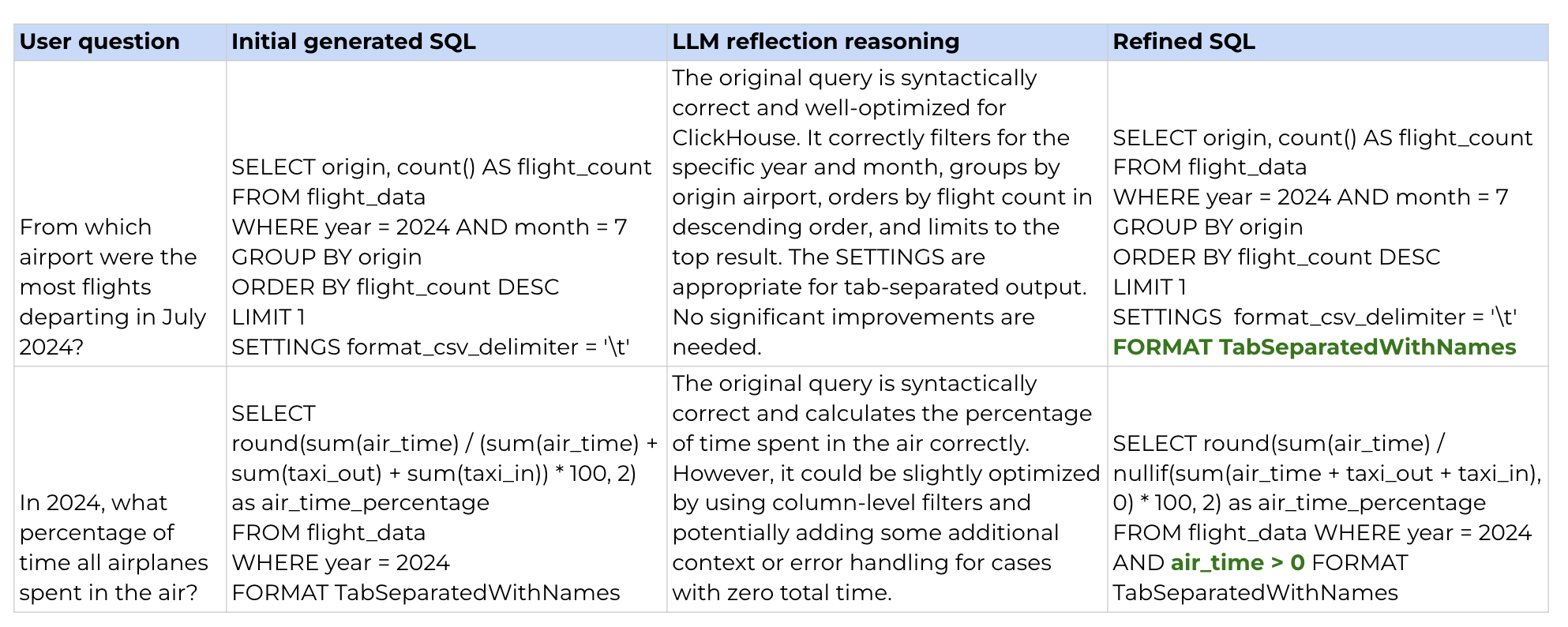
Nonetheless, there are additionally circumstances the place the LLM overcomplicated the reply. The preliminary SQL was appropriate (matching the golden set reply), however then the LLM determined to ‘enhance’ it. A few of these enhancements are cheap (e.g., accounting for nulls or excluding cancelled flights). Nonetheless, for some cause, it determined to make use of ClickHouse sampling, regardless that we don’t have a lot knowledge and our desk doesn’t help sampling. In consequence, the refined question returned an execution error: Database returned the next error: Code: 141. DB::Exception: Storage default.flight_data would not help sampling. (SAMPLING_NOT_SUPPORTED).

Reflection with exterior suggestions
Reflection didn’t enhance accuracy a lot. That is probably as a result of we didn’t present any further info that might assist the mannequin generate a greater consequence. Let’s strive sharing exterior suggestions with the mannequin:
The results of our verify on whether or not the format is specified accurately
The output from the database (both knowledge or an error message)
Let’s put collectively a immediate for this and generate a brand new model of the SQL.
feedback_reflection_user_prompt_template = '''
Your activity is to evaluate the SQL question generated by one other analyst and suggest enhancements if needed.
Examine whether or not the question is syntactically appropriate and optimized for efficiency.
Take note of nuances in knowledge (particularly time stamps varieties, whether or not to make use of complete elapsed time or time within the air, and so forth).
Be certain that the question solutions the preliminary person query precisely.
Because the consequence return the next JSON:
{{
'reasoning': '',
'refined_sql': ''
}}
Be certain that ONLY JSON is within the output and nothing else. Be certain that the output JSON is legitimate.
Right here is the preliminary person question:
{user_query}
Right here is the SQL question generated by one other analyst:
{sql}
Right here is the database output of this question:
{output}
We run an computerized verify on the SQL question to verify whether or not it has fomatting points. This is the output:
{formatting}
'''
def feedback_reflection(rec) -> str:
# outline message for formatting
if 'No format laid out in SQL' in rec['llm_direct_sql_quality_heuristics']:
formatting = 'SQL lacking formatting. Specify "format TabSeparatedWithNames" to make sure that column names are additionally returned'
else:
formatting = 'Formatting is appropriate'
# establishing a person immediate
user_prompt = feedback_reflection_user_prompt_template.format(
user_query = rec['question'],
sql = rec['llm_direct_sql'],
output = rec['llm_direct_output'],
formatting = formatting
)
# making an LLM name
message = shopper.messages.create(
mannequin = "claude-3-5-haiku-latest",
max_tokens = 8192,
system = base_sql_system_prompt,
messages = [
{'role': 'user', 'content': user_prompt}
]
)
knowledge = message.content material[0].textual content
# strip markdown code blocks
knowledge = knowledge.strip()
if knowledge.startswith('```json'):
knowledge = knowledge[7:]
elif knowledge.startswith('```'):
knowledge = knowledge[3:]
if knowledge.endswith('```'):
knowledge = knowledge[:-3]
knowledge = knowledge.strip()
return json.hundreds(knowledge.substitute('n', ' ')) After operating our accuracy measurements, we will see that accuracy has improved considerably: 17 appropriate solutions (85% accuracy) in comparison with 14 (70% accuracy).
If we verify the circumstances the place the LLM fastened the problems, we will see that it was capable of appropriate the format, handle SQL execution errors, and even revise the enterprise logic (e.g., utilizing air time for calculating velocity).

Let’s additionally do some error evaluation to look at the circumstances the place the LLM made errors. Within the desk under, we will see that the LLM struggled with defining sure timestamps, incorrectly calculating complete time, or utilizing complete time as a substitute of air time for velocity calculations. Nonetheless, among the discrepancies are a bit tough:
- Within the final question, the time interval wasn’t explicitly outlined, so it’s cheap for the LLM to make use of 2010–2023. I wouldn’t take into account this an error, and I’d alter the analysis as a substitute.
- One other instance is easy methods to outline airline velocity:
avg(distance/time)orsum(distance)/sum(time). Each choices are legitimate since nothing was specified within the person question or system immediate (assuming we don’t have a predefined calculation methodology).

General, I believe we achieved a reasonably good consequence. Our remaining 85% accuracy represents a major 15% level enchancment. You might doubtlessly transcend one iteration and run 2–3 rounds of reflection, nevertheless it’s value assessing once you hit diminishing returns in your particular case, since every iteration goes with elevated price and latency.
You will discover the total code on GitHub.
Abstract
It’s time to wrap issues up. On this article, we began our journey into understanding how the magic of agentic AI methods works. To determine it out, we’ll implement a multi-agent text-to-data software utilizing solely API calls to basis fashions. Alongside the best way, we’ll stroll by means of the important thing design patterns step-by-step: beginning at present with reflection, and transferring on to software use, planning, and multi-agent coordination.
On this article, we began with essentially the most basic sample — reflection. Reflection is on the core of any agentic move, because the LLM must mirror on its progress towards attaining the top purpose.
Reflection is a comparatively easy sample. We merely ask the identical or a distinct mannequin to analyse the consequence and try to enhance it. As we realized in follow, sharing exterior suggestions with the mannequin (like outcomes from static checks or database output) considerably improves accuracy. A number of analysis research and our personal expertise with the text-to-SQL agent show the advantages of reflection. Nonetheless, these accuracy good points come at a price: extra tokens spent and better latency on account of a number of API calls.
Thanks for studying. I hope this text was insightful. Keep in mind Einstein’s recommendation: “The essential factor is to not cease questioning. Curiosity has its personal cause for current.” Could your curiosity lead you to your subsequent nice perception.
Reference
This text is impressed by the “Agentic AI” course by Andrew Ng from DeepLearning.AI.