Picture by Creator
# Introduction
The flexibility to gather high-quality, related info remains to be a core talent for any knowledge skilled. Whereas there are a number of methods to assemble knowledge, one of the crucial highly effective and reliable strategies is thru APIs (utility programming interfaces). They function bridges, permitting completely different software program programs to speak and share knowledge seamlessly.
On this article, we’ll break down the necessities of utilizing APIs for knowledge assortment — why they matter, how they work, and easy methods to get began with them in Python.
# What’s an API?
An API (utility programming interface) is a algorithm and protocols that permits completely different software program programs to speak and trade knowledge effectively.
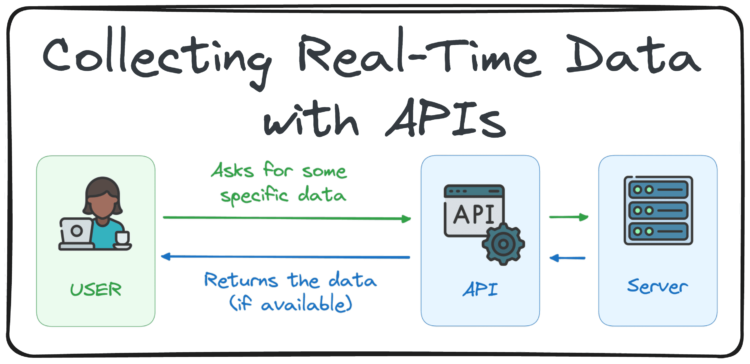
Consider it like eating at a restaurant. As a substitute of talking on to the chef, you place your order with a waiter. The waiter checks if the substances can be found, passes the request to the kitchen, and brings your meal again as soon as it’s prepared.
An API works the identical method: it receives your request for particular knowledge, checks if that knowledge exists, and returns it if out there — serving because the messenger between you and the info supply.
When utilizing an API, interactions sometimes contain the next elements:
- Consumer: The applying or system that sends a request to entry knowledge or performance
- Request: The shopper sends a structured request to the server, specifying what knowledge it wants
- Server: The system that processes the request and offers the requested knowledge or performs an motion
- Response: The server processes the request and sends again the info or end in a structured format, often JSON or XML


Picture by Creator
This communication permits functions to share info or functionalities effectively, enabling duties like fetching knowledge from a database or interacting with third-party providers.
# Why Utilizing APIs for Knowledge Assortment?
APIs provide a number of benefits for knowledge assortment:
- Effectivity: They supply direct entry to knowledge, eliminating the necessity for guide knowledge gathering
- Actual-time Entry: APIs usually ship up-to-date info, which is crucial for time-sensitive analyses
- Automation: They permit automated knowledge retrieval processes, decreasing human intervention and potential errors
- Scalability: APIs can deal with massive volumes of requests, making them appropriate for in depth knowledge assortment duties
# Implementing API Calls in Python
Making a fundamental API name in Python is likely one of the best and most sensible workout routines to get began with knowledge assortment. The favored requests library makes it easy to ship HTTP requests and deal with responses.
To exhibit the way it works, we’ll use the Random Person Generator API, a free service that gives dummy person knowledge in JSON format, good for testing and studying.
Right here’s a step-by-step information to creating your first API name in Python.
// Putting in the Requests Library:
// Importing the Required Libraries:
import requests
import pandas as pd
// Checking the Documentation Web page:
Earlier than making any requests, it is vital to know how the API works. This consists of reviewing out there endpoints, parameters, and response construction. Begin by visiting the Random Person API documentation.
// Defining the API Endpoint and Parameters:
Primarily based on the documentation, we will assemble a easy request. On this instance, we fetch person knowledge restricted to customers from america:
url="https://randomuser.me/api/"
params = {'nat': 'us'}
// Making the GET Request:
Use the requests.get() operate with the URL and parameters:
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
// Dealing with the Response:
Verify whether or not the request was profitable, then course of the info:
if response.status_code == 200:
knowledge = response.json()
# Course of the info as wanted
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code}")
// Changing Our Knowledge right into a Dataframe:
To work with the info simply, we will convert it right into a pandas DataFrame:
knowledge = response.json()
df = pd.json_normalize(knowledge["results"])
df
Now, let’s exemplify it with an actual case.
# Working with the Eurostat API
Eurostat is the statistical workplace of the European Union. It offers high-quality, harmonized statistics on a variety of matters corresponding to economics, demographics, atmosphere, business, and tourism — masking all EU member states.
By way of its API, Eurostat gives public entry to an unlimited assortment of datasets in machine-readable codecs, making it a worthwhile useful resource for knowledge professionals, researchers, and builders involved in analyzing European-level knowledge.
// Step 0: Understanding the Knowledge within the API:
If you happen to go verify the Knowledge part of Eurostat, you’ll find a navigation tree. We will attempt to determine some knowledge of curiosity within the following subsections:
- Detailed Datasets: Full Eurostat knowledge in multi-dimensional format
- Chosen Datasets: Simplified datasets with fewer indicators, in 2–3 dimensions
- EU Insurance policies: Knowledge grouped by particular EU coverage areas
- Cross-cutting: Thematic knowledge compiled from a number of sources
// Step 1: Checking the Documentation:
All the time begin with the documentation. Yow will discover Eurostat’s API information right here. It explains the API construction, out there endpoints, and easy methods to kind legitimate requests.


// Step 2: Producing the First Name Request:
To generate an API request utilizing Python, step one is putting in and importing the requests library. Bear in mind, we already put in it within the earlier easy instance. Then, we will simply generate a name request utilizing a demo dataset from the Eurostat documentation.
# We import the requests library
import requests
# Outline the URL endpoint -> We use the demo URL within the EUROSTATS API documentation.
url = "https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/api/dissemination/statistics/1.0/knowledge/DEMO_R_D3DENS?lang=EN"
# Make the GET request
response = requests.get(url)
# Print the standing code and response knowledge
print(f"Standing Code: {response.status_code}")
print(response.json()) # Print the JSON response
Professional tip: We will cut up the URL into the bottom URL and parameters to make it simpler to perceive what knowledge we are requesting from the API.
# We import the requests library
import requests
# Outline the URL endpoint -> We use the demo URL within the EUROSTATS API documentation.
url = "https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/api/dissemination/statistics/1.0/knowledge/DEMO_R_D3DENS"
# Outline the parameters -> We outline the parameters so as to add within the URL.
params = {
'lang': 'EN' # Specify the language as English
}
# Make the GET request
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
# Print the standing code and response knowledge
print(f"Standing Code: {response.status_code}")
print(response.json()) # Print the JSON response
// Step 3: Figuring out Which Dataset to Name:
As a substitute of utilizing the demo dataset, you may choose any dataset from the Eurostat database. For instance, let’s question the dataset TOUR_OCC_ARN2, which accommodates tourism lodging knowledge.
# We import the requests library
import requests
# Outline the URL endpoint -> We use the demo URL within the EUROSTATS API documentation.
base_url = "https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/api/dissemination/statistics/1.0/knowledge/"
dataset = "TOUR_OCC_ARN2"
url = base_url + dataset
# Outline the parameters -> We outline the parameters so as to add within the URL.
params = {
'lang': 'EN' # Specify the language as English
}
# Make the GET request -> we generate the request and procure the response
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
# Print the standing code and response knowledge
print(f"Standing Code: {response.status_code}")
print(response.json()) # Print the JSON response
// Step 4: Understanding the Response
Eurostat’s API returns knowledge in JSON-stat format, a normal for multidimensional statistical knowledge. It can save you the response to a file and discover its construction:
import requests
import json
# Outline the URL endpoint and dataset
base_url = "https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/api/dissemination/statistics/1.0/knowledge/"
dataset = "TOUR_OCC_ARN2"
url = base_url + dataset
# Outline the parameters so as to add within the URL
params = {
'lang': 'EN',
"time": 2019 # Specify the language as English
}
# Make the GET request and procure the response
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
# Verify the standing code and deal with the response
if response.status_code == 200:
# Parse the JSON response
knowledge = response.json()
# Generate a JSON file and write the response knowledge into it
with open("eurostat_response.json", "w") as json_file:
json.dump(knowledge, json_file, indent=4) # Save JSON with fairly formatting
print("JSON file 'eurostat_response.json' has been efficiently created.")
else:
print(f"Error: Obtained standing code {response.status_code} from the API.")
// Step 5: Remodeling the Response into Usable Knowledge:
Now that we acquired the info, we will discover a method to put it aside right into a tabular format (CSV) to clean the method of analyzing it.
import requests
import pandas as pd
# Step 1: Make the GET request to the Eurostat API
base_url = "https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/api/dissemination/statistics/1.0/knowledge/"
dataset = "TOUR_OCC_ARN2" # Vacationer lodging statistics dataset
url = base_url + dataset
params = {'lang': 'EN'} # Request knowledge in English
# Make the API request
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
# Step 2: Verify if the request was profitable
if response.status_code == 200:
knowledge = response.json()
# Step 3: Extract the size and metadata
dimensions = knowledge['dimension']
dimension_order = knowledge['id'] # ['geo', 'time', 'unit', 'indic', etc.]
# Extract labels for every dimension dynamically
dimension_labels = {dim: dimensions[dim]['category']['label'] for dim in dimension_order}
# Step 4: Decide the scale of every dimension
dimension_sizes = {dim: len(dimensions[dim]['category']['index']) for dim in dimension_order}
# Step 5: Create a mapping for every index to its respective label
# For instance, if we've 'geo', 'time', 'unit', and 'indic', map every index to the proper label
index_labels = {
dim: record(dimension_labels[dim].keys())
for dim in dimension_order
}
# Step 6: Create a listing of rows for the CSV
rows = []
for key, worth in knowledge['value'].gadgets():
# `key` is a string like '123', we have to break it down into the corresponding labels
index = int(key) # Convert string index to integer
# Calculate the indices for every dimension
indices = {}
for dim in reversed(dimension_order):
dim_index = index % dimension_sizes[dim]
indices[dim] = index_labels[dim][dim_index]
index //= dimension_sizes[dim]
# Assemble a row with labels from all dimensions
row = {f"{dim.capitalize()} Code": indices[dim] for dim in dimension_order}
row.replace({f"{dim.capitalize()} Title": dimension_labels[dim][indices[dim]] for dim in dimension_order})
row["Value (Tourist Accommodations)"] = worth
rows.append(row)
# Step 7: Create a DataFrame and reserve it as CSV
if rows:
df = pd.DataFrame(rows)
csv_filename = "eurostat_tourist_accommodation.csv"
df.to_csv(csv_filename, index=False)
print(f"CSV file '{csv_filename}' has been efficiently created.")
else:
print("No legitimate knowledge to save lots of as CSV.")
else:
print(f"Error: Obtained standing code {response.status_code} from the API.")
// Step 6: Producing a Particular View
Think about we simply wish to hold these information similar to Campings, Flats or Lodges. We will generate a closing desk with this situation, and procure a pandas DataFrame we will work with.
# Verify the distinctive values within the 'Nace_r2 Title' column
set(df["Nace_r2 Name"])
# Listing of choices to filter
choices = ['Camping grounds, recreational vehicle parks and trailer parks',
'Holiday and other short-stay accommodation',
'Hotels and similar accommodation']
# Filter the DataFrame primarily based on whether or not the 'Nace_r2 Title' column values are within the choices record
df = df[df["Nace_r2 Name"].isin(choices)]
df
# Greatest Practices When Working with APIs
- Learn the Docs: All the time verify the official API documentation to know endpoints and parameters
- Deal with Errors: Use conditionals and logging to gracefully deal with failed requests
- Respect Charge Limits: Keep away from overwhelming the server — verify if charge limits apply
- Safe Credentials: If the API requires authentication, by no means expose your API keys in public code
# Wrapping Up
Eurostat’s API is a robust gateway to a wealth of structured, high-quality European statistics. By studying easy methods to navigate its construction, question datasets, and interpret responses, you may automate entry to vital knowledge for evaluation, analysis, or decision-making — proper out of your Python scripts.
You’ll be able to go verify the corresponding code in my GitHub repository My-Articles-Pleasant-Hyperlinks
Josep Ferrer is an analytics engineer from Barcelona. He graduated in physics engineering and is at present working within the knowledge science subject utilized to human mobility. He’s a part-time content material creator targeted on knowledge science and expertise. Josep writes on all issues AI, masking the appliance of the continued explosion within the subject.